成都html5网站建设上海十大营销策划公司排名
C++实现线程池
- 一、前言
- 二、线程池的接口设计
- 2.1、类封装
- 2.2、线程池的初始化
- 2.3、线程池的启动
- 2.4、线程池的停止
- 2.5、线程的执行函数run()
- 2.6、任务的运行函数
- 2.7、等待所有线程结束
- 三、测试线程池
- 四、源码地址
- 总结
一、前言
C++实现的线程池,可能涉及以下知识点:
- decltype。
- packaged_task。
- make_shared。
- mutex。
- unique_lock。
- notify_one。
- future。
- queue。
- bind。
- thread。
等等。
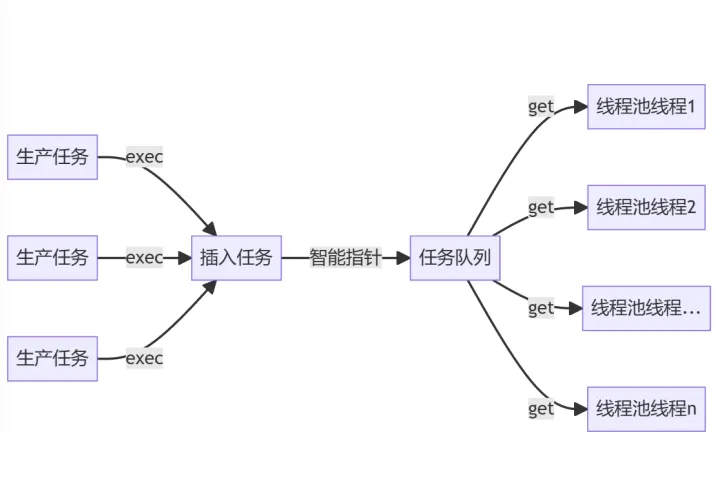
二、线程池的接口设计
(1)封装一个线程池的类。
(2)线程池的初始化:设置线程的数量。
(3)启动线程池:创建线程等工作。
(4)执行任务的函数。
(5)停止线程池。
(6)等所有任务执行完成,退出执行函数。
2.1、类封装
线程池类,采用c++11来实现。
#ifndef _CPP_THREAD_POOL_H_
#define _CPP_THREAD_POOL_H_#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <queue>
#include <mutex>
#include <vector>
#include <thread>
#include <future>#ifdef WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#else
#include <sys/time.h>
#endifusing namespace std;void getNow(timeval *tv);
int64_t getNowMs();#define TNOW getNow()
#define TNOWMS getNowMs()class CPP_ThreadPool{
protected:struct TaskFunc{TaskFunc(uint64_t expireTime):_expireTime(expireTime){}int64_t _expireTime=0;//超时的绝对时间function<void()> _func;};typedef shared_ptr<TaskFunc> TaskFuncPtr;/* * @brief 获取任务 ** *@return TaskFuncPtr */bool get(TaskFuncPtr& task);/** @brief 线程池是否退出*/bool isTerminate(){return _bTerminate;}/** @brief 线程运行态*/void run();public: /** @brief 构造函数 */CPP_ThreadPool(); /* * @brief 析构, 会停止所有线程 */virtual ~CPP_ThreadPool();/* * * @brief 初始化. * * @param num 工作线程个数 */bool init(size_t num);/** @brief 停止所有线程, 会等待所有线程结束 */void stop();/** @brief 启动所有线程 */bool start();/* * @brief 等待当前任务队列中, 所有工作全部结束(队列无任务). * @param millsecond 等待的时间(ms), -1:永远等待 * @return true, 所有工作都处理完毕 * false,超时退出 */bool waitForAllDone(int millsecond=-1);/** @brief 获取线程个数.* @return size_t 线程个数 */size_t getThreadNum(){unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);return _threads.size();}/** @brief 获取当前线程池的任务数* @return size_t 线程池的任务数 */size_t getJobNum(){unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);return _tasks.size();}/** @brief 用线程池启用任务(F是function, Args是参数) ** * @param ParentFunctor * @param tf * @return 返回任务的future对象, 可以通过这个对象来获取返回值 */template <class F,class... Args>auto exec(F&& f, Args&&... args)->future<decltype(f(args...))>{return exec(0,f,args...);}/* * unused.** @brief 用线程池启用任务(F是function, Args是参数) * @param 超时时间 ,单位ms (为0时不做超时控制) ;若任务超时,此任务将被丢弃 * @param bind function * @return 返回任务的future对象, 可以通过这个对象来获取返回值 ** template <class F, class... Args> * 它是c++里新增的最强大的特性之一,它对参数进行了高度泛化,它能表示0到任意个数、任意类型的参数 * auto exec(F &&f, Args &&... args) -> std::future<decltype(f(args...))> * std::future<decltype(f(args...))>:返回future,调用者可以通过future获取返回值 * 返回值后置*/template<class F,class... Args>auto exec(int64_t timeoutMs,F&& f,Args&&... args) -> future<decltype(f(args...))>{//获取现在时间int64_t expireTime=(timeoutMs==0)?0:TNOWMS+timeoutMs;// 定义返回值类型using retType=decltype(f(args...));// 封装任务auto task=make_shared<packaged_task<retType()>>(bind(forward<F>(f),forward<Args>(args)...));// 封装任务指针,设置过期时间TaskFuncPtr fPtr=make_shared<TaskFunc>(expireTime);fPtr->_func=[task](){(*task)();};unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);// 插入任务_tasks.push(fPtr);// 唤醒阻塞的线程,可以考虑只有任务队列为空的情 况再去notify_condition.notify_one();return task->get_future();}protected:size_t _threadNum;//线程数量bool _bTerminate;//判定是否终止线程池mutex _mutex; //唯一锁vector<thread*> _threads; //工作线程数组queue<TaskFuncPtr> _tasks; //任务队列condition_variable _condition;//条件变量atomic<int> _atomic{0};//原子变量
};#endif
使用示例:
CPP_ThreadPool tpool;
tpool.init(5); //初始化线程池线程数
//启动线程方式
tpool.start();
//将任务丢到线程池中*
tpool.exec(testFunction, 10); //参数和start相同
//等待线程池结束
tpool.waitForAllDone(1000); //参数<0时, 表示无限等待(注意有人调用stop也会推出)
//此时: 外部需要结束线程池是调用
tpool.stop();
注意:ZERO_ThreadPool::exec执行任务返回的是个future, 因此可以通过future异步获取结果, 比如:
int testInt(int i)
{ return i;
}
auto f = tpool.exec(testInt, 5);
cout << f.get() << endl; //当testInt在线程池中执行后, f.get()会返回数值5 class Test
{
public: int test(int i);
};
Test t;
auto f = tpool.exec(std::bind(&Test::test, &t, std::placeholders::_1), 10);
//返回的future对象, 可以检查是否执行
cout << f.get() << endl;
2.2、线程池的初始化
主要是设置线程池中线程的数量,如果线程池已经存在则直接返回,防止重复初始化。
bool CPP_ThreadPool::init(size_t num)
{unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);if(!_threads.empty())return false;_threadNum=num;return true;
}
2.3、线程池的启动
根据设置的线程数量,创建线程并保存在一个数组中。如果线程池已经存在则直接返回,防止重复启动。
bool CPP_ThreadPool::start()
{unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);if(!_threads.empty())return false;for(size_t i=0;i<_threadNum;i++){_threads.push_back(new thread(&CPP_ThreadPool::run,this));}return true;
}
2.4、线程池的停止
设置线程退出条件,并通知所有线程。停止时,要等待所有线程都执行完任务,再销毁线程。
需要注意锁的粒度。
void CPP_ThreadPool::stop()
{// 注意要有这个{},不然会死锁。{unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);_bTerminate=true;_condition.notify_all();}size_t thdCount=_threads.size();for(size_t i=0;i<thdCount;i++){if(_threads[i]->joinable()){_threads[i]->join();}delete _threads[i];_threads[i]=NULL;}unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);_threads.clear();
}
2.5、线程的执行函数run()
读取任务:判断任务是否存在,如果任务队列为空,则进入等待状态直到任务队列不为空或退出线程池(这里需要两次判断,因为可能存在虚假唤醒)。
执行任务:调用匿名函数。
检测所有任务都是否执行完毕:这里使用了原子变量来检测任务是否都执行完,原因在于任务队列为空不代表任务已经执行完(任务可能还在运行中、也可能是任务刚弹出还没运行),使用原子变量来计数就更严谨。
bool CPP_ThreadPool::get(TaskFuncPtr& task)
{unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);if(_tasks.empty())//判断任务是否存在{_condition.wait(lock,[this]{return _bTerminate || !_tasks.empty();//唤醒条件});}if(_bTerminate)return false;if(!_tasks.empty())//判断任务是否存在{task=move(_tasks.front());// 使用移动语义_tasks.pop();//弹出一个任务return true;}return false;
}// 执行任务的线程
void CPP_ThreadPool::run()
{while(!isTerminate()){TaskFuncPtr task;// 读取任务bool ok=get(task);if(ok){++_atomic;try{if(task->_expireTime!=0 && task->_expireTime < TNOWMS){// 处理超时任务}elsetask->_func();//执行任务}catch(...){}--_atomic;// 任务执行完毕,这里只是为了通知waitForAllDoneunique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);if(_atomic==0 && _tasks.empty())_condition.notify_all();}}
}
2.6、任务的运行函数
这里使用了可变模块参数、智能指针、bind、function、捕获列表的相关技术知识。
返回任务的future对象, 可以通过这个对象来获取返回值。
超时时间 ,单位ms (为0时不做超时控制) ;若任务超时,此任务将被丢弃。
可变模块参数对参数进行了高度泛化,它能表示0到任意个数、任意类型的参数。
/** @brief 用线程池启用任务(F是function, Args是参数) ** * @param ParentFunctor * @param tf * @return 返回任务的future对象, 可以通过这个对象来获取返回值 */template <class F,class... Args>auto exec(F&& f, Args&&... args)->future<decltype(f(args...))>{return exec(0,f,args...);}/* * unused.** @brief 用线程池启用任务(F是function, Args是参数) * @param 超时时间 ,单位ms (为0时不做超时控制) ;若任务超时,此任务将被丢弃 * @param bind function * @return 返回任务的future对象, 可以通过这个对象来获取返回值 ** template <class F, class... Args> * 它是c++里新增的最强大的特性之一,它对参数进行了高度泛化,它能表示0到任意个数、任意类型的参数 * auto exec(F &&f, Args &&... args) -> std::future<decltype(f(args...))> * std::future<decltype(f(args...))>:返回future,调用者可以通过future获取返回值 * 返回值后置*/template<class F,class... Args>auto exec(int64_t timeoutMs,F&& f,Args&&... args) -> future<decltype(f(args...))>{//获取现在时间int64_t expireTime=(timeoutMs==0)?0:TNOWMS+timeoutMs;// 定义返回值类型using retType=decltype(f(args...));// 封装任务auto task=make_shared<packaged_task<retType()>>(bind(forward<F>(f),forward<Args>(args)...));// 封装任务指针,设置过期时间TaskFuncPtr fPtr=make_shared<TaskFunc>(expireTime);fPtr->_func=[task](){(*task)();};unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);// 插入任务_tasks.push(fPtr);// 唤醒阻塞的线程,可以考虑只有任务队列为空的情 况再去notify_condition.notify_one();return task->get_future();}
2.7、等待所有线程结束
bool CPP_ThreadPool::waitForAllDone(int millsecond)
{unique_lock<mutex> lock(_mutex);if(_tasks.empty())return true;if(millsecond<0){_condition.wait(lock,[this]{ return _tasks.empty();});return true;}else{return _condition.wait_for(lock,chrono::milliseconds(millsecond),[this]{ return _tasks.empty();});}
}
三、测试线程池
#include <iostream>
#include "cppThreadPool.h"using namespace std;void func1(int a)
{ cout << "func1() a=" << a << endl;
}
void func2(int a, string b)
{ cout << "func2() a=" << a << ", b=" << b<< endl;
}void func3()
{cout<<"func3"<<endl;
}void test01()
{cout<<"test 01"<<endl;CPP_ThreadPool threadpool;threadpool.init(2);threadpool.start();//启动线程池// 执行任务threadpool.exec(func1,10);threadpool.exec(func2,20,"FLY.");threadpool.exec(1000,func3);threadpool.waitForAllDone();threadpool.stop();
}int func1_future(int a)
{ cout << "func1() a=" << a << endl; return a;
}string func2_future(int a, string b)
{ cout << "func2() a=" << a << ", b=" << b<< endl; return b;
}void test02()
{cout<<"test 02"<<endl;CPP_ThreadPool threadpool;threadpool.init(2);threadpool.start();//启动线程池future<decltype(func1_future(0))> ret01=threadpool.exec(func1_future,10);future<string> ret02=threadpool.exec(func2_future,20,"FLY.");threadpool.waitForAllDone();cout<<"ret01 = "<<ret01.get()<<endl;cout<<"ret02 = "<<ret02.get()<<endl;threadpool.stop();}class Test{
public:int test(int a){cout<<_name<<": a = "<<a<<endl;return a+1;}void setname(string name){_name=name;}string _name;};void test03()
{cout<<"test 03"<<endl;CPP_ThreadPool threadpool;threadpool.init(2);threadpool.start();//启动线程池Test t1;Test t2;t1.setname("Test 1");t2.setname("Test 2");auto f1=threadpool.exec(bind(&Test::test,&t1,placeholders::_1),10);auto f2=threadpool.exec(bind(&Test::test,&t2,placeholders::_1),20);threadpool.waitForAllDone();cout<<"f1 = "<<f1.get()<<endl;cout<<"f2 = "<<f2.get()<<endl;threadpool.stop();}int main(int argc,char **argv)
{// 简单测试线程池test01();// 测试任务函数返回值test02();// 测试类对象函数的绑定test03();return 0;
}
执行结果:
test 01
func1() a=10
func2() a=20, b=FLY.
func3
test 02
func1() a=10
func2() a=20, b=FLY.
ret01 = 10
ret02 = FLY.
test 03
Test 1: a = 10
Test 2: a = 20
f1 = 11
f2 = 21
四、源码地址
源码已经上传github。
总结
线程池的核心:初始化、线程启动、执行函数、线程停止。

