音乐盒的网站怎么做客户关系管理系统
文章目录
- Input & Output
- Variables & Data types
- Python字符串重复(字符串乘法)
- 字符串和数字连接在一起print时,要强制类型转换int为str
- 用input()得到的用户输入,是str类型,如果要以int形式计算的话,需要强制类型转换为int
- 我们可以只使用一个变量user_input来节省内存
- convert string type to date type
- convert date to string
- Multi-line code statement 换行符
- 在括号内,行的延续的自动的
- Escape sequence 转义字符
- String format
- string format 中限制输入占位大小的同时小数点后位数
- Arithmetic operators
- Fundamentals of the Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency
- Algorithm analysis framework 算法分析框架
- 1. Measuring Input Sizes
- 2. Units for Measuring Running Time
- 3. Order of growth
- 4. Worst-Case, Best-Case, and Average-Case Efficiency
- Summary
- 渐进式符号
- no faster
- at least as fast as
- at same rate
- Summary
- Some Properties
- Using Limits for Comparing Orders of Growth
- Analysis of non-recursive algorithms 非递归算法的分析
- Analysis of recursive algorithms 递归算法的分析
- Examples
- 求n!
- 重要的递归类型
- For-loop
- 字符串操作
- 字符串内容大写/小写
- 找字串位置,找不到返回-1
- 字符串长度
- 根据下标返回字符串中对应字符
- 切割字符串
- Data Structure
- Abstract data type (ADT)
- Function 函数
- 四舍五入保留小数点后多少位函数
- min,max函数是python内置的
- random函数
- Class and object
- Instance attribute vs Class attribute
- Instance method vs Class/Static method
- Instance method
- Special instance method
- `__init__` 方法
- `__str__` 方法
- `__repr__` 方法
- 完整示例
- Static / Class method
- Class method vs static method: 类方法和静态方法的区别
- 类方法(Class Method)
- 静态方法(Static Method)
- 示例代码:
- Defining class and creating object 定义类和创建对象
- Accessing object instance attributes 访问对象的实例属性
- Modify object instance attributes 更改对象的实例属性
- Defining an object instance method 定义对象的示例属性
- 类注释和函数注释
- 案例学习:定义一个学生类
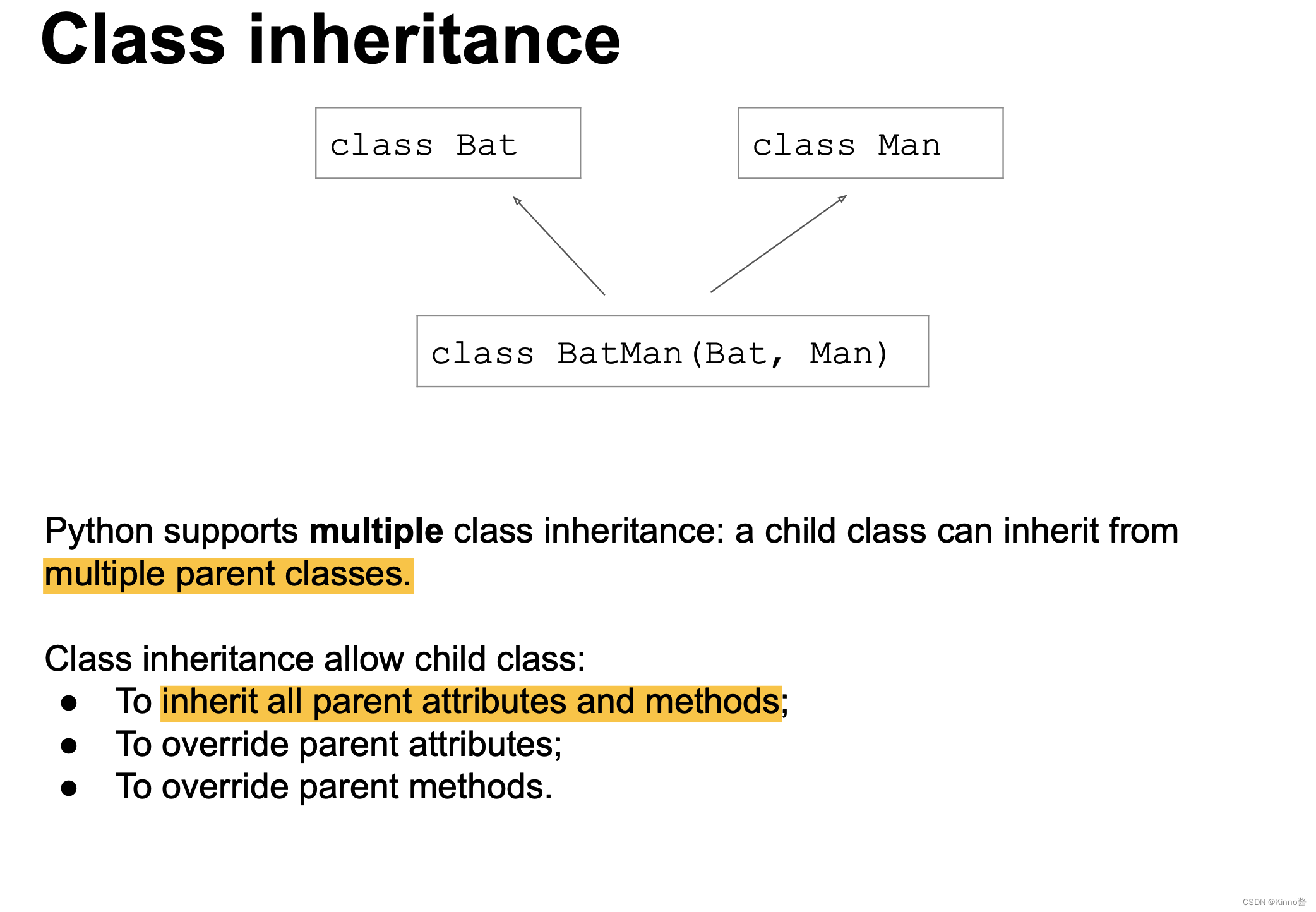
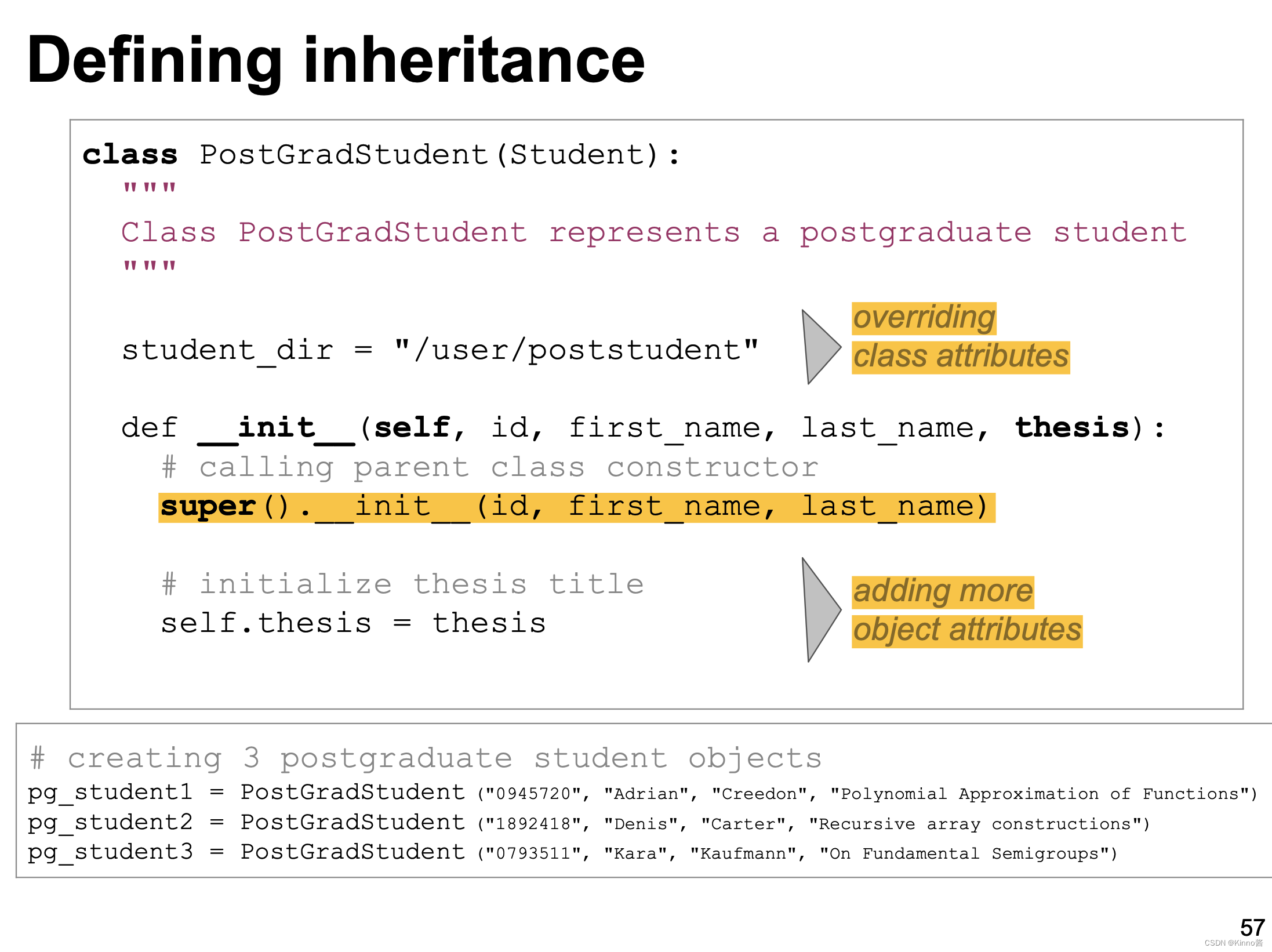
- Class inheritance 类继承
- Array and Linked List
- Numpy Array
- Python链表实现
- Debuging
- Exception&traceback
- Assertion
- Logging
Input & Output

Variables & Data types
str: a string represents a sequence of characters.
int: an integer, a whole number
float: a decimal number
bool: a boolean value is either True or False.
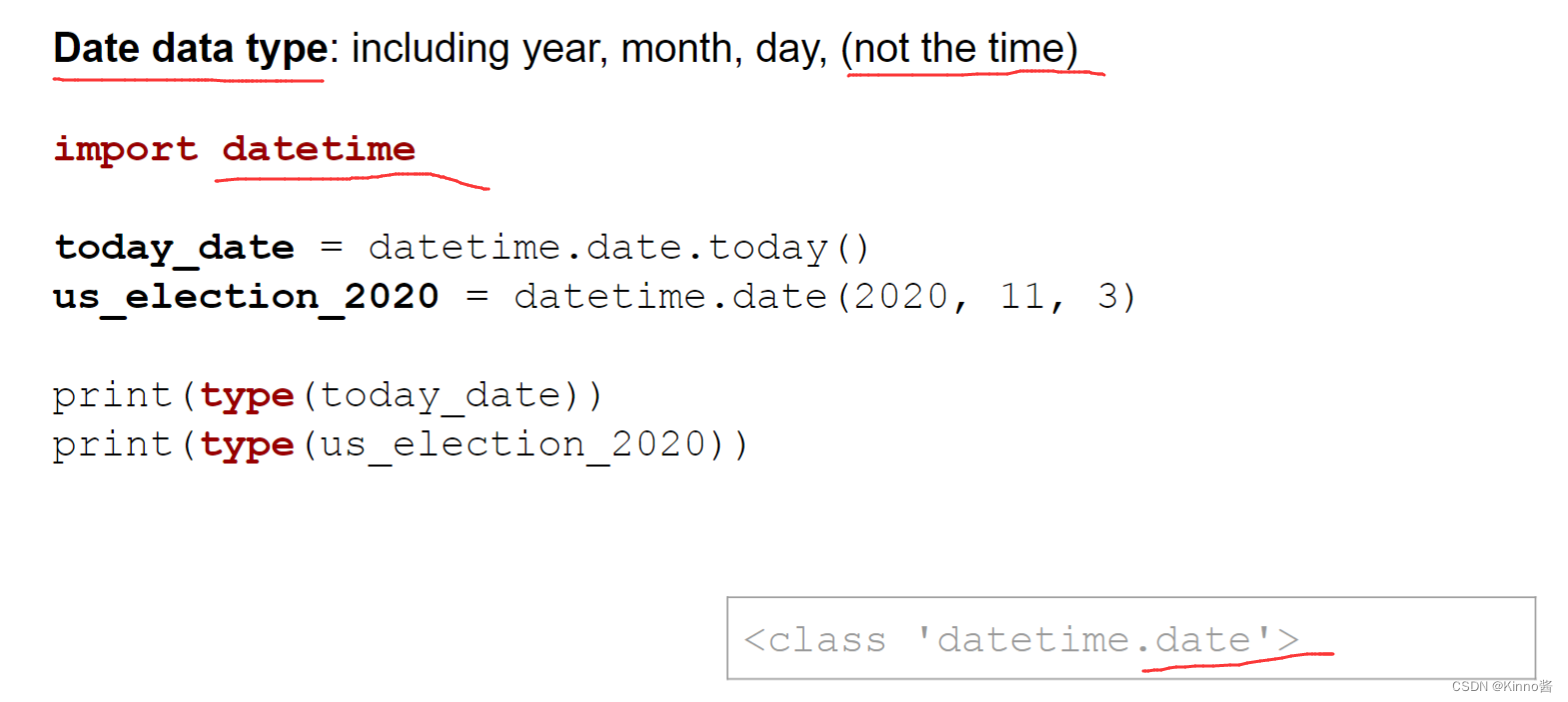
Date data type: including year, month, day, (not the time)
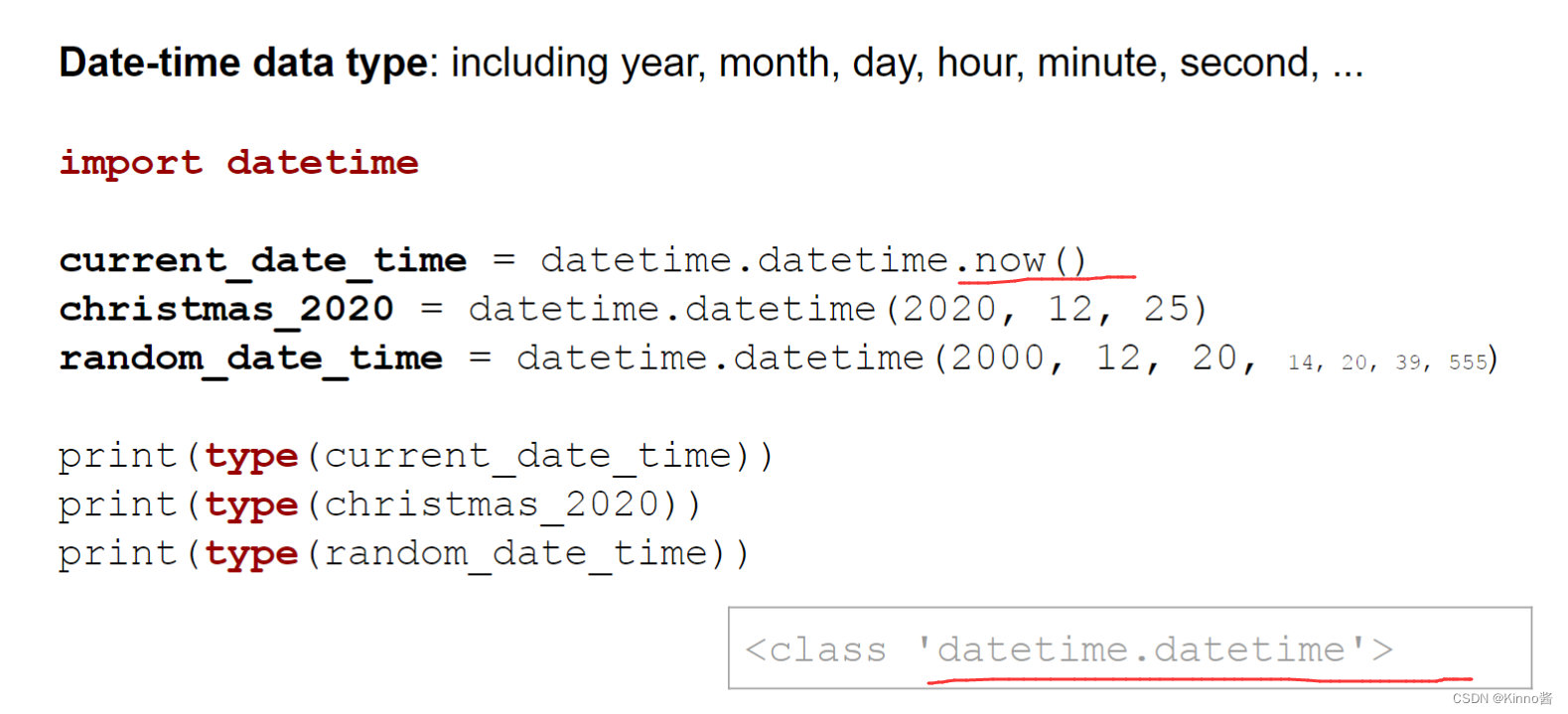
Date-time data type: including year, month, day, hour, minute, second, …

Python字符串重复(字符串乘法)

字符串和数字连接在一起print时,要强制类型转换int为str


用input()得到的用户输入,是str类型,如果要以int形式计算的话,需要强制类型转换为int

我们可以只使用一个变量user_input来节省内存

convert string type to date type
strptime

convert date to string
strftime

Multi-line code statement 换行符

在括号内,行的延续的自动的
Line continuation is automatic when the split comes while a
statement is inside parenthesis ( , brackets [ or braces {

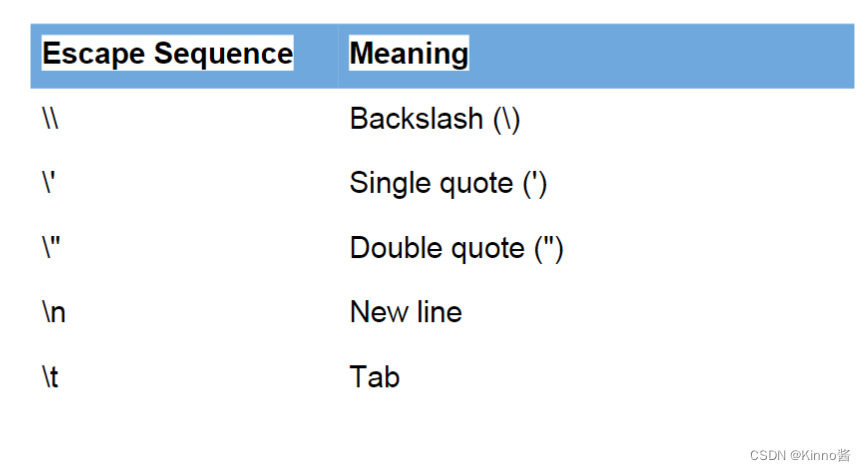
Escape sequence 转义字符



String format

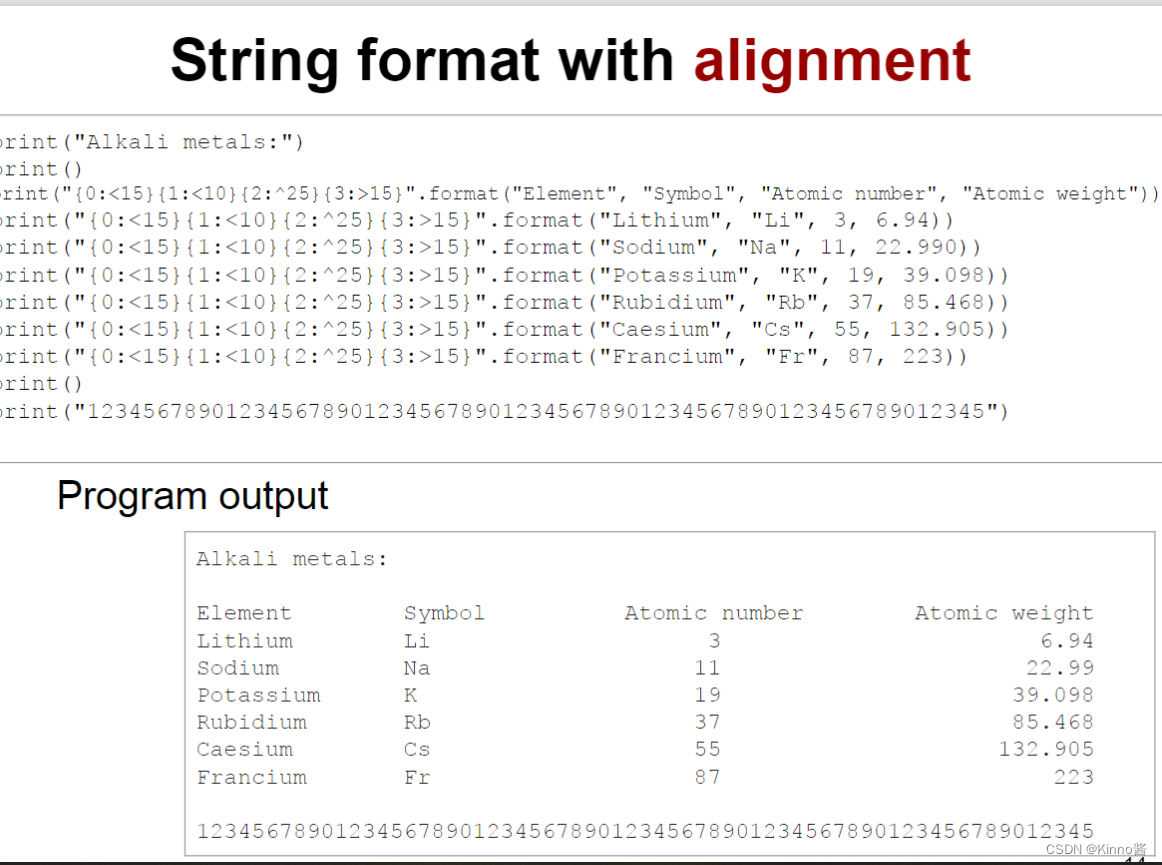
| 格式 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| <15 | left alignment, using 15 spaces |
| ^25 | center alignment, using 25 spaces |
| >15 | right alignment, using 15 spaces |
string format 中限制输入占位大小的同时小数点后位数
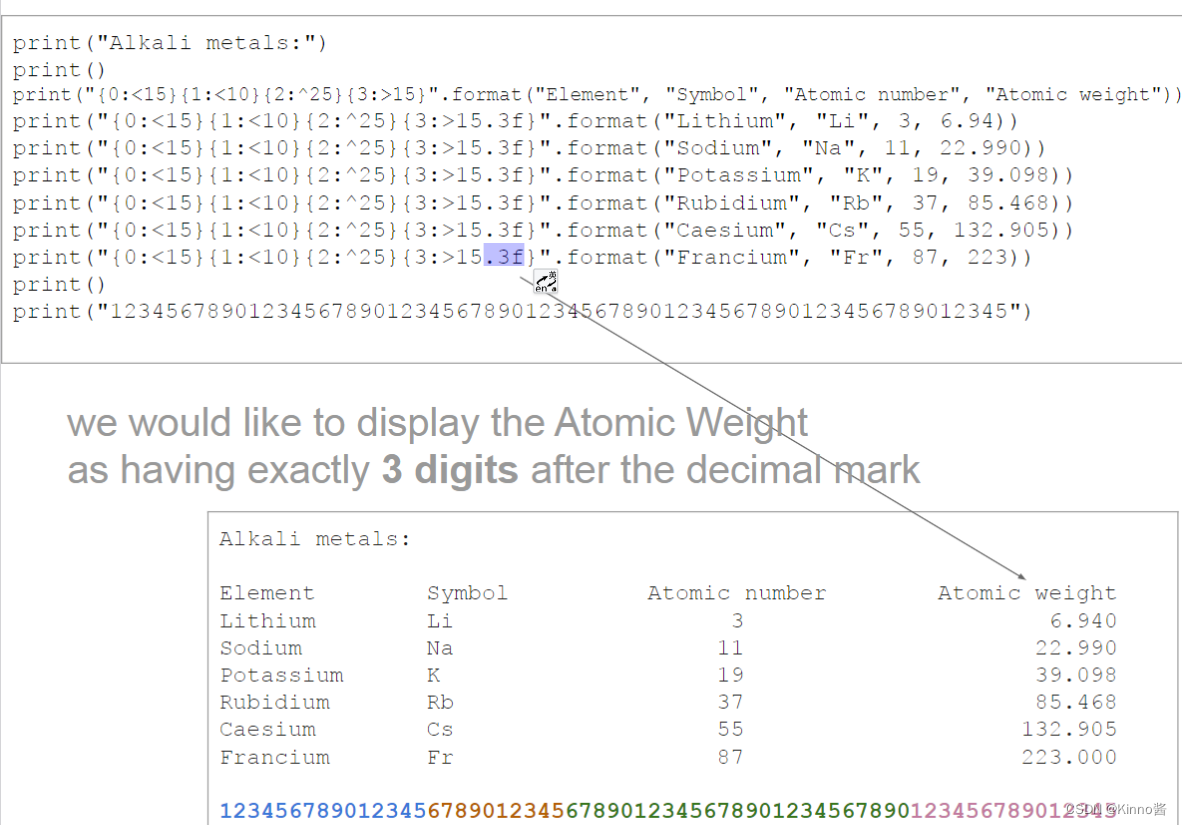
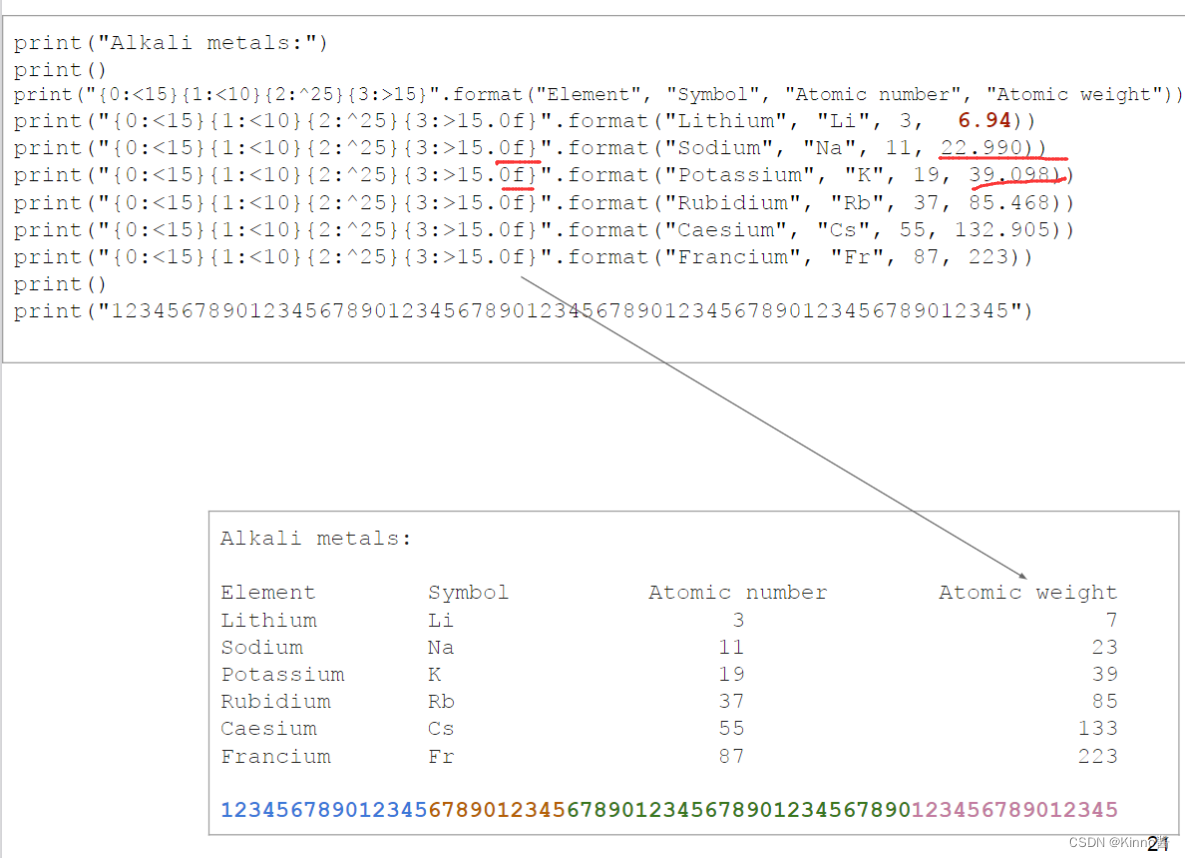
还可以通过这种方式实现四舍五入取整
.0f
Arithmetic operators
Floor division = 地板除 = 向下取整除
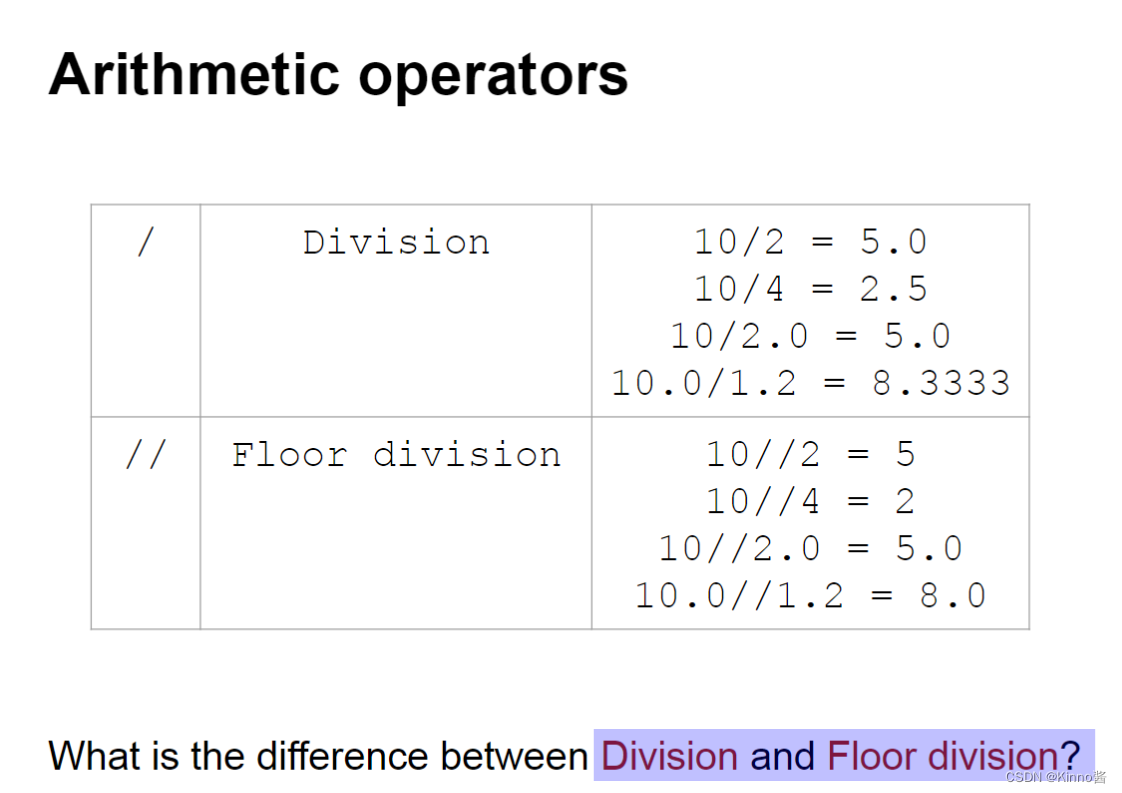
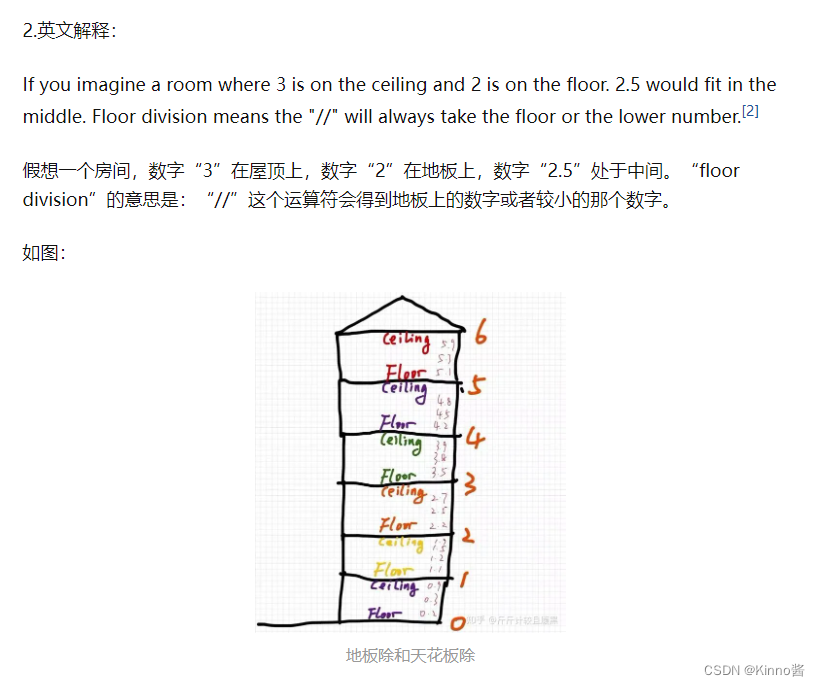
floor division地板除是什么意思
向下取整除,就是地板除 floor division
向上取整除,就是天花板除,ceil division
来自 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/221901326
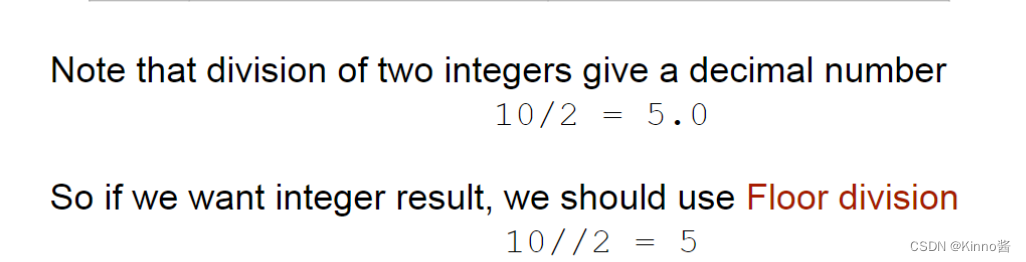

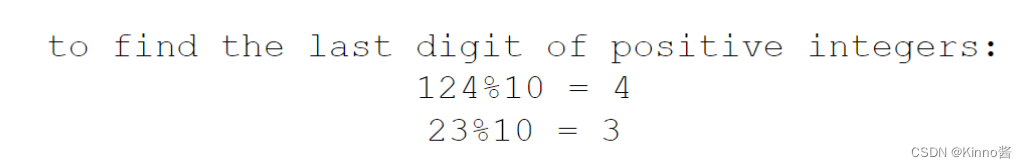
Fundamentals of the Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency
Algorithm analysis framework 算法分析框架
Analysis of algorithms means to investigate an algorithm’s efficiency with respect to resources: running time and memory space
算法分析是指研究一个算法在资源方面的效率:运行时间和内存空间。

1. Measuring Input Sizes
Efficiency is defined as a function of input size.
F(n)
2. Units for Measuring Running Time
Count the number of times an algorithm’s basic operation is executed
计算一个算法的基本操作被执行的次数
Basic operation: the operation that contributes the most to the total
running time.
例如,基本操作通常是算法最内部循环中最耗时的操作。
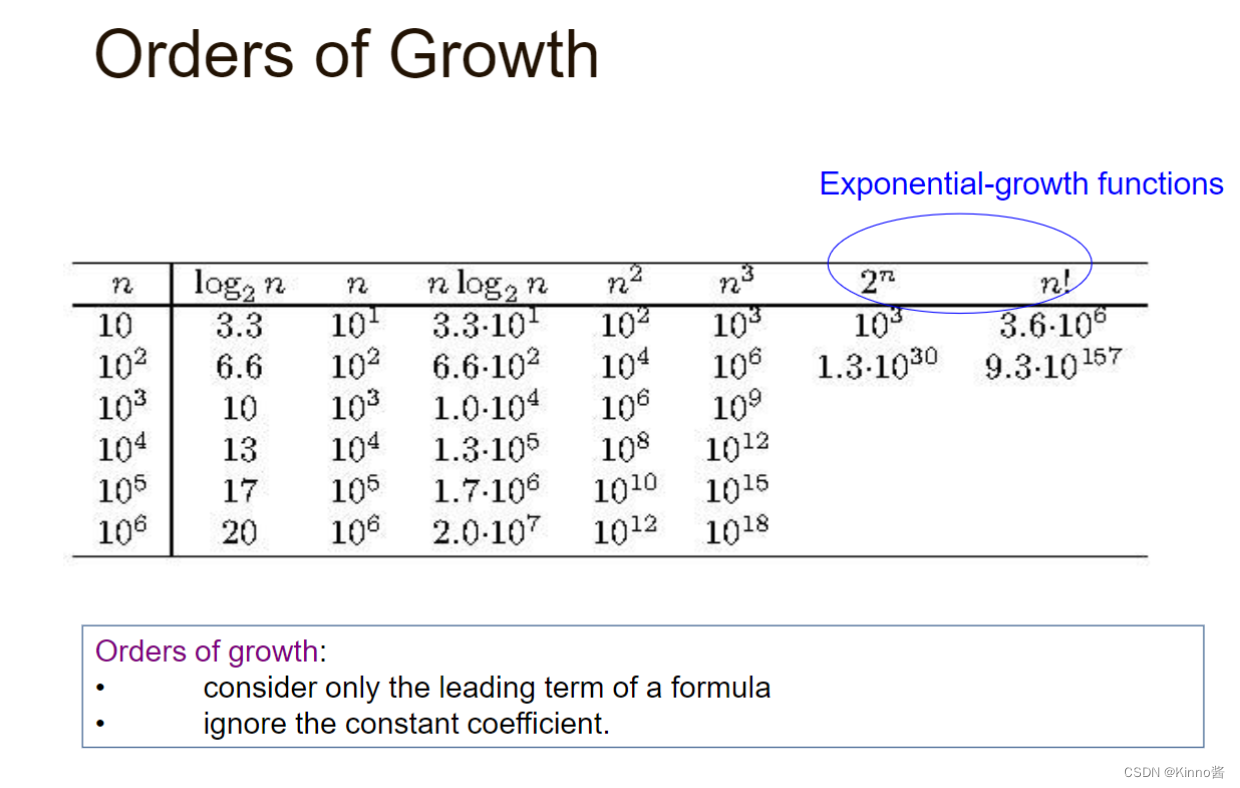
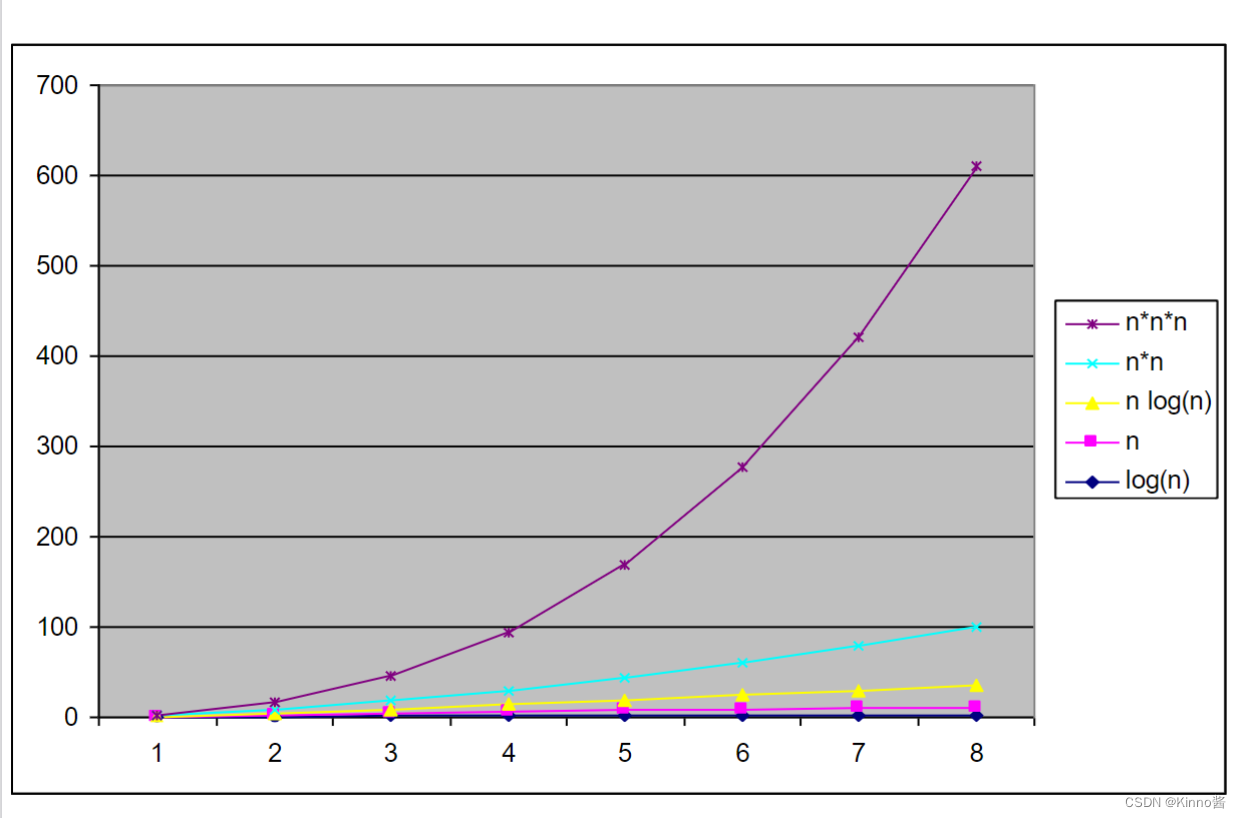
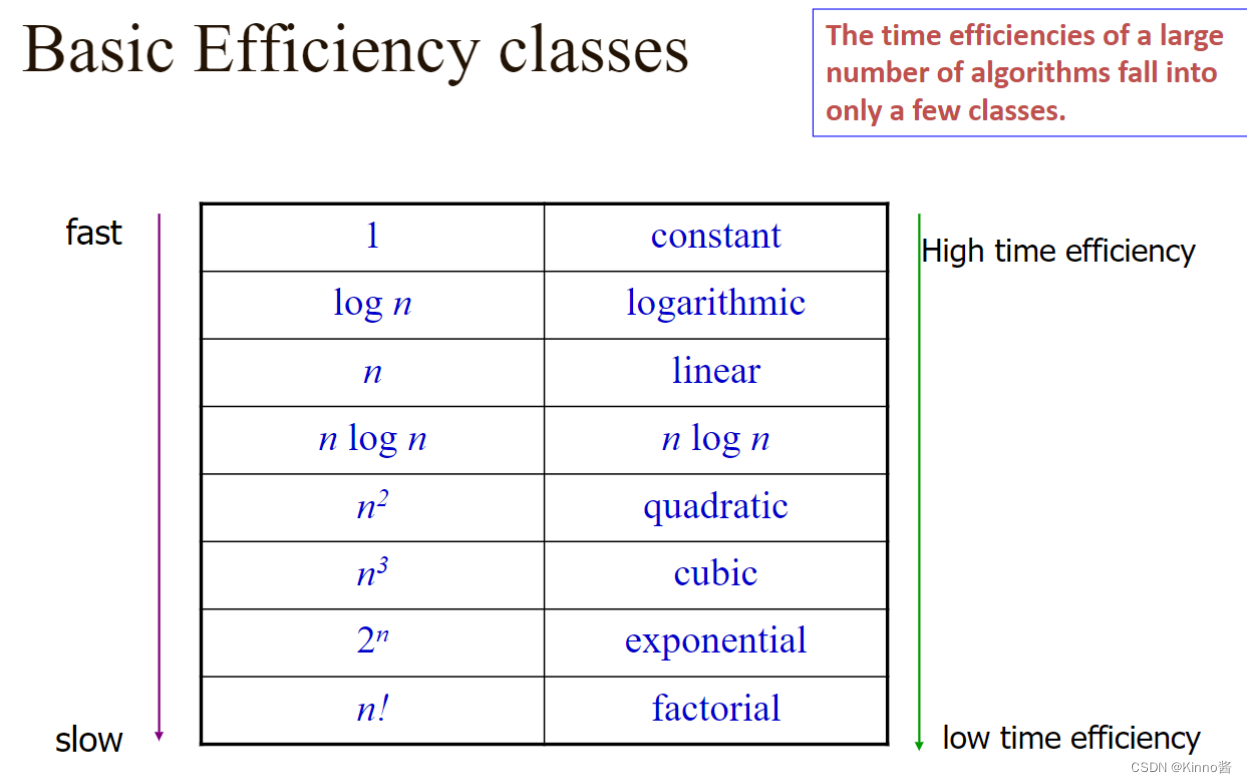
3. Order of growth
4. Worst-Case, Best-Case, and Average-Case Efficiency

==Efficiency (# of times the basic operation will be executed) ==

Average case:
Efficiency (#of times the basic operation will be executed) for a typical/random
input of size n. NOT the average of worst and best case. How to find the
average case efficiency?
平均情况。对于大小为n的典型/随机输入的效率(基本操作将被执行的次数),而不是最坏和最好情况的平均值。如何找到平均案例的效率?
Summary
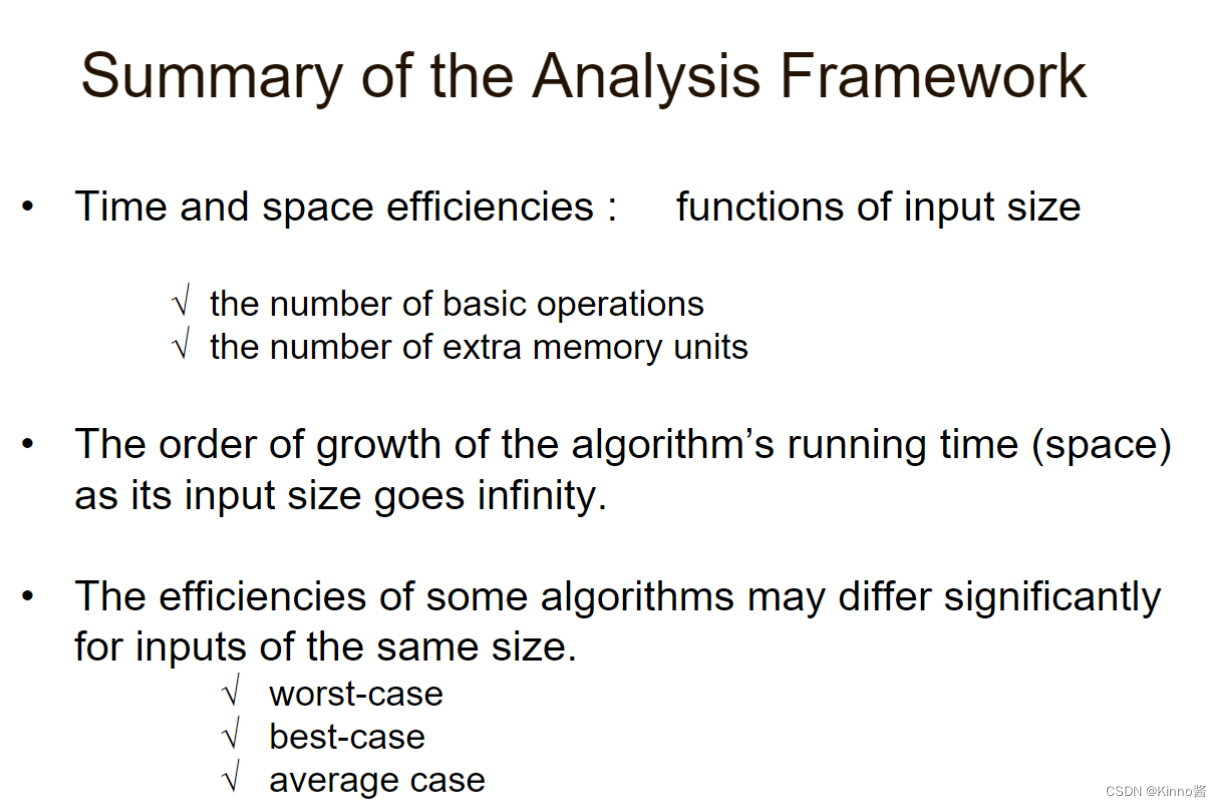
算法的运行时间(空间)随着其输入大小的增加而增长的阶数为无穷大。
对于相同大小的输入,一些算法的效率可能有很大的不同
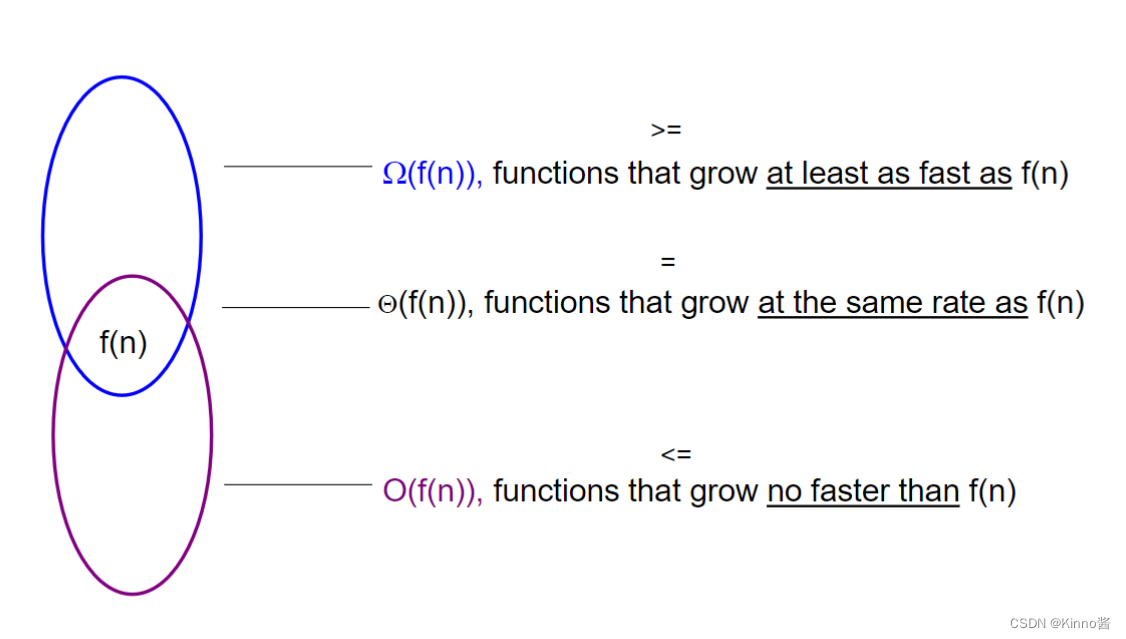
渐进式符号

no faster
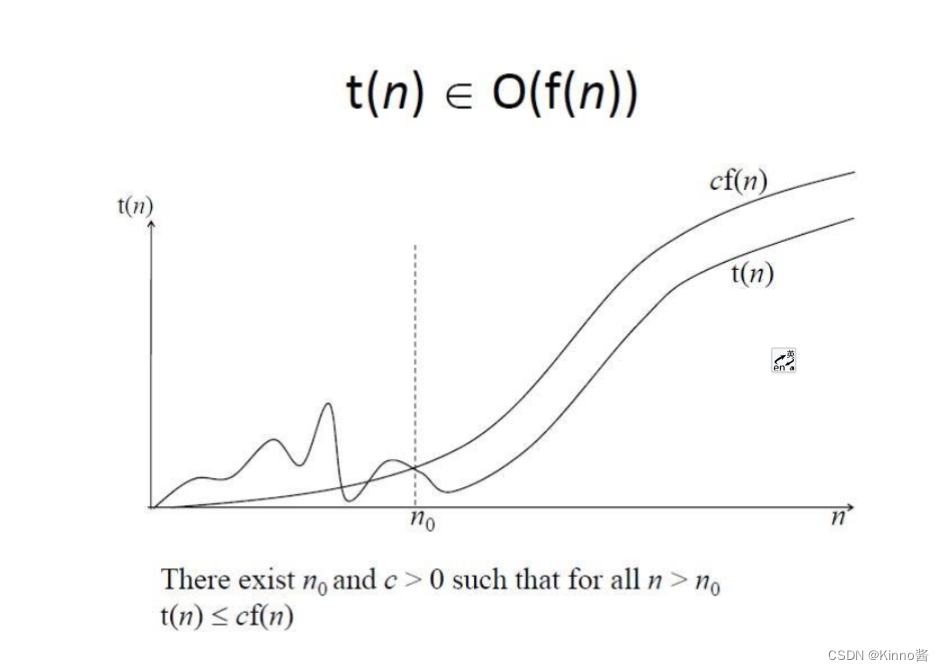

at least as fast as
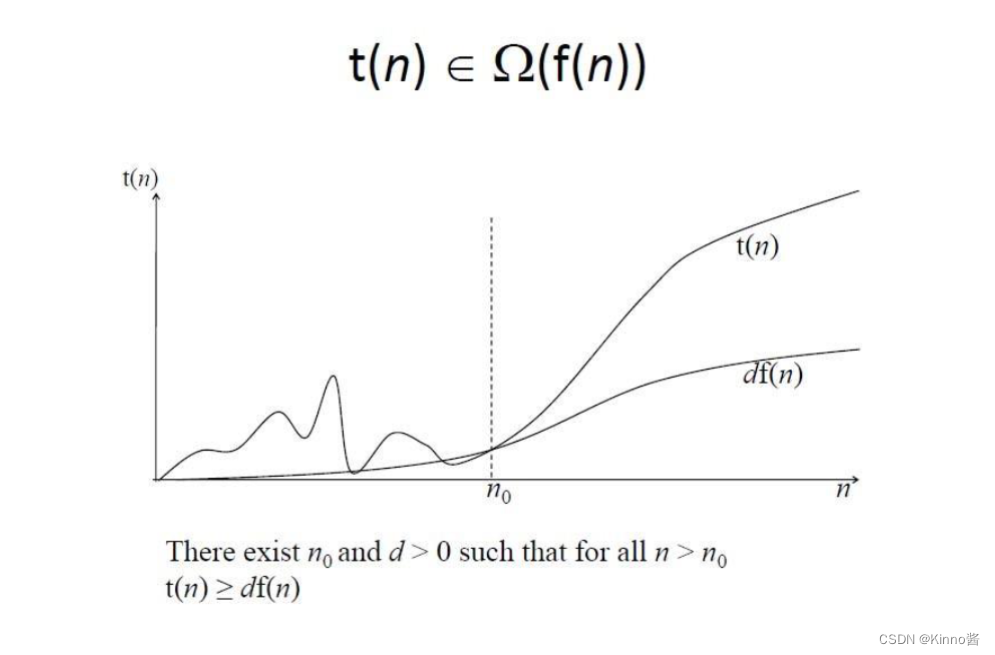

at same rate
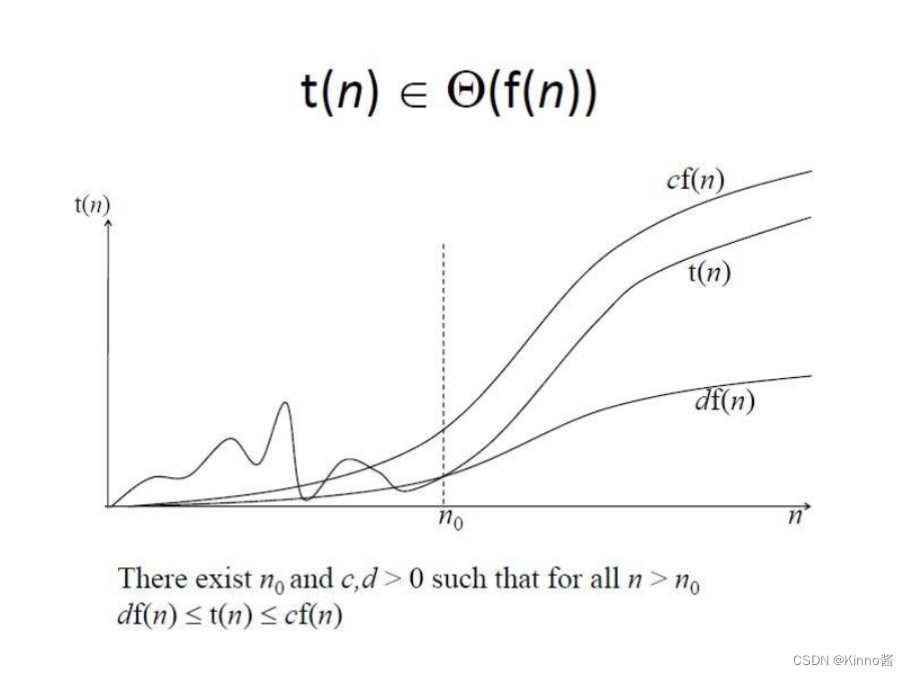

Summary
Some Properties
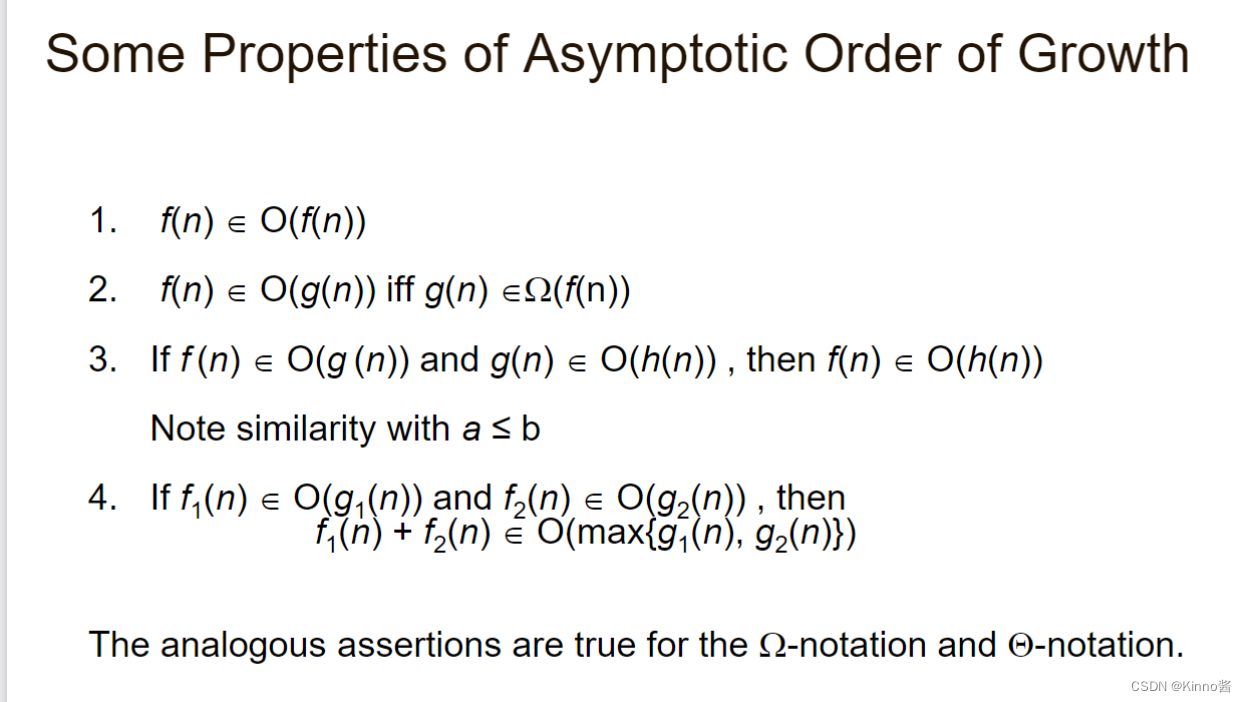

意义:算法的整体效率将由增长顺序较大的部分决定。
Using Limits for Comparing Orders of Growth
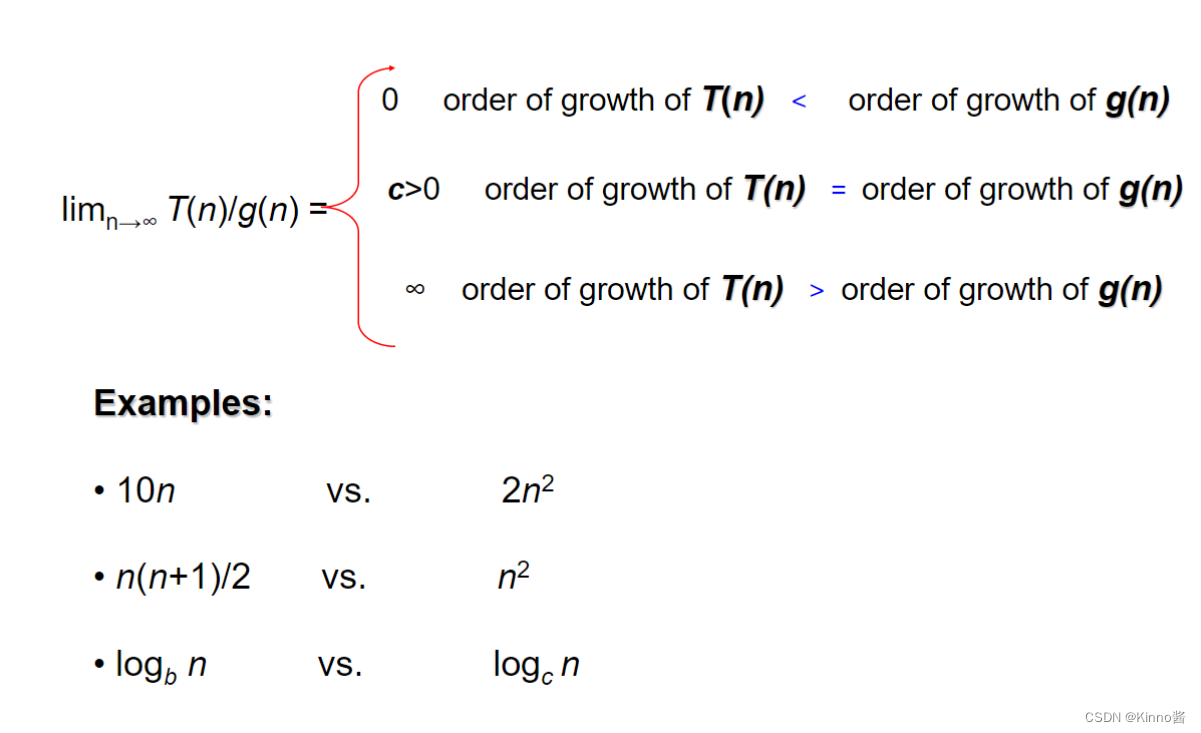
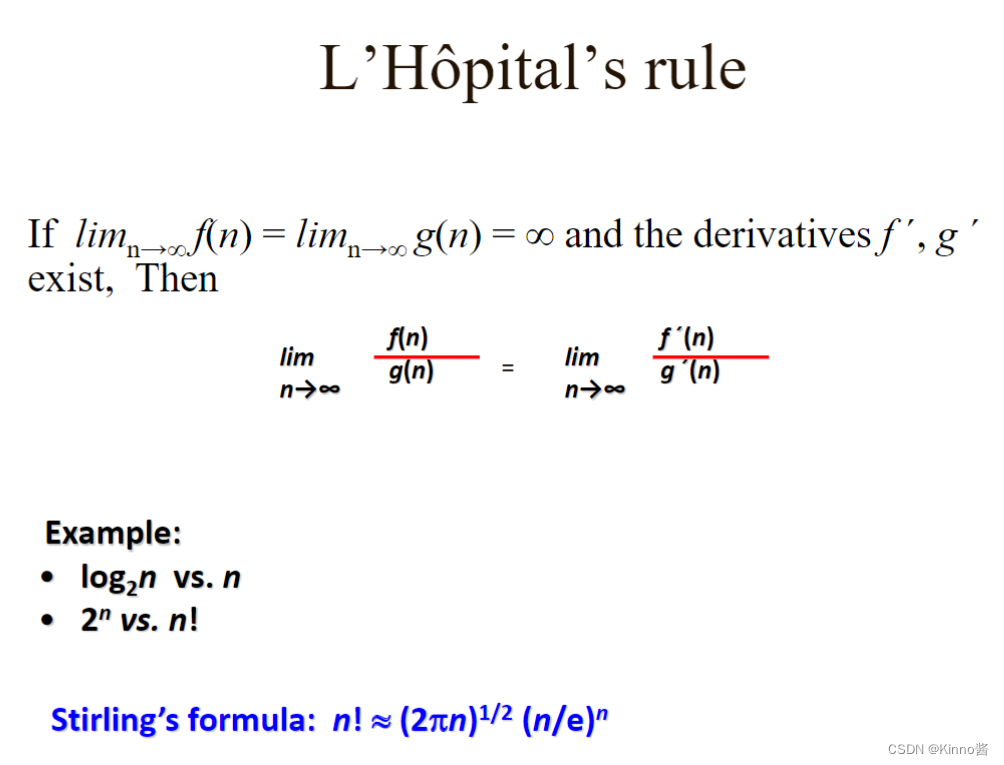
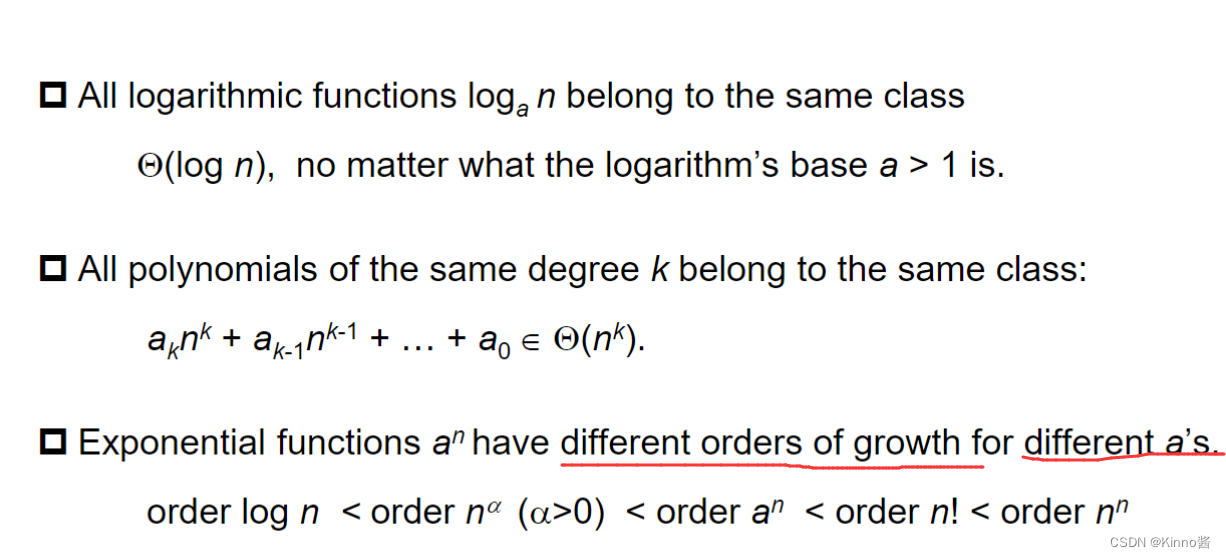
所有的对数函数loga n都属于同一个类别
所有相同度数k的多项式都属于同一类别
指数函数对于不同的a有不同的增长顺序
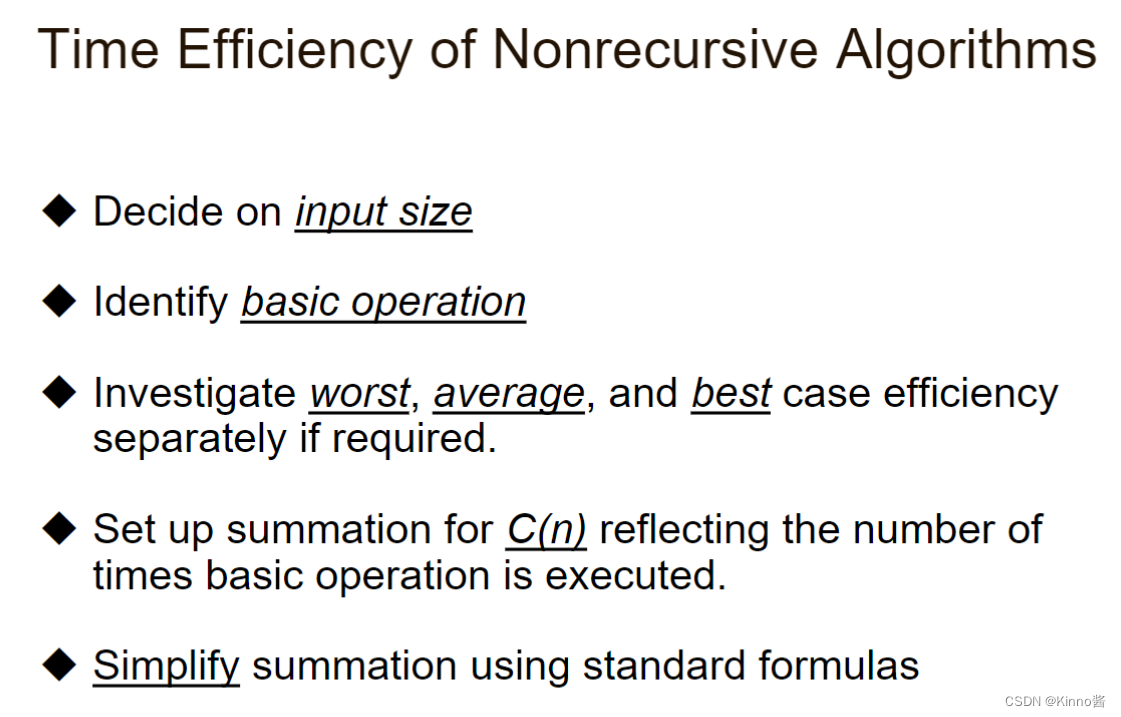
Analysis of non-recursive algorithms 非递归算法的分析
Analysis of recursive algorithms 递归算法的分析

- 计算递归调用的次数
- 解决递归问题,或通过后向替代或其他方法估计解决方案的数量级
Examples
求n!
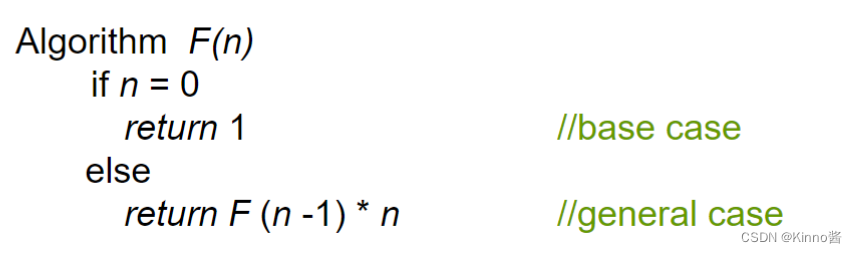

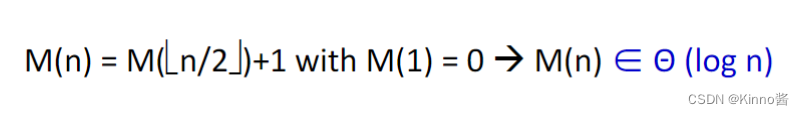
重要的递归类型


For-loop

range(0,10) 范围是左闭右开
字符串操作
字符串内容大写/小写

.upper()
.lower()
找字串位置,找不到返回-1

字符串长度

根据下标返回字符串中对应字符

切割字符串

[i:j] 范围左开右闭,从下标为i的字符到下标为j-1的字符,获得的子串长度为j-i
Data Structure
data, relationship , operation

Abstract data type (ADT)

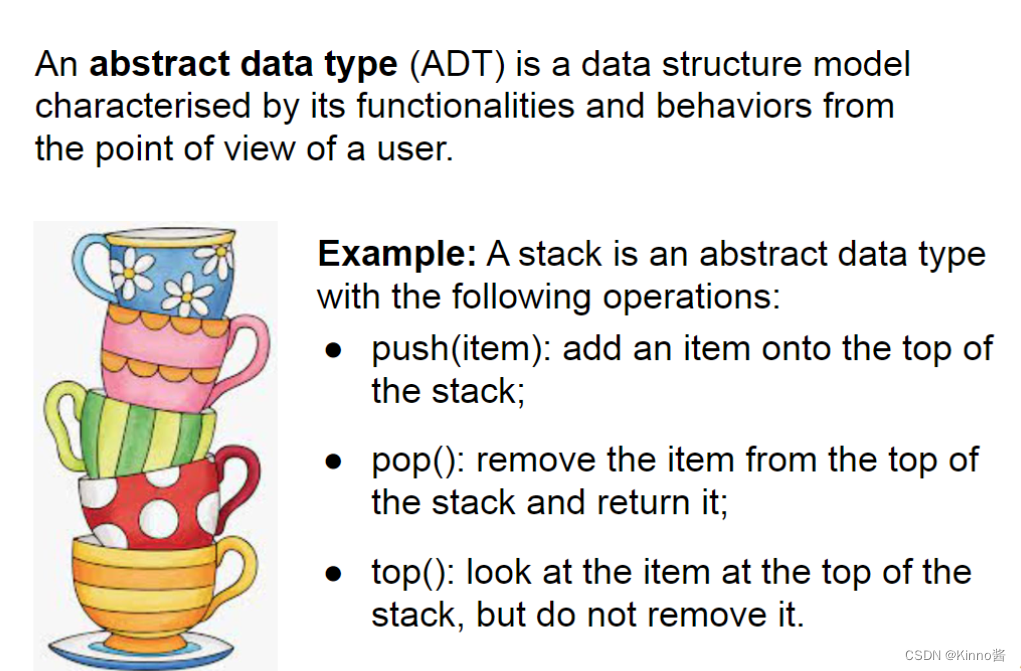

Function 函数


四舍五入保留小数点后多少位函数
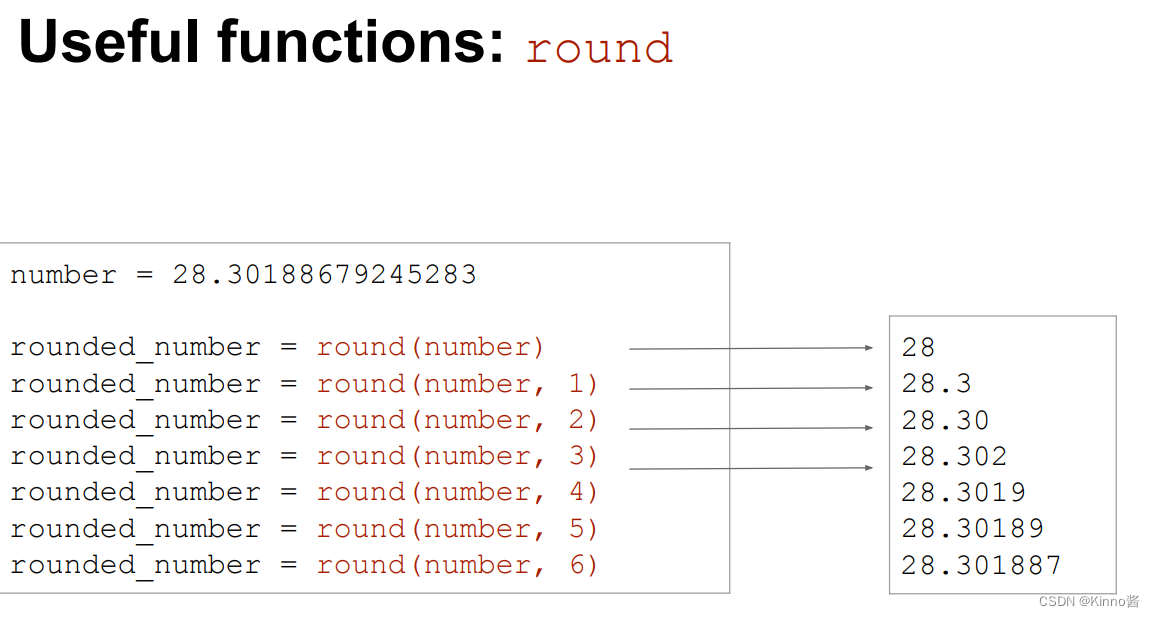
min,max函数是python内置的

random函数

左闭右闭
Class and object
对象是类的实例。
术语“对象”和“实例”可以互换使用。每个对象实例都有自己的数据值。

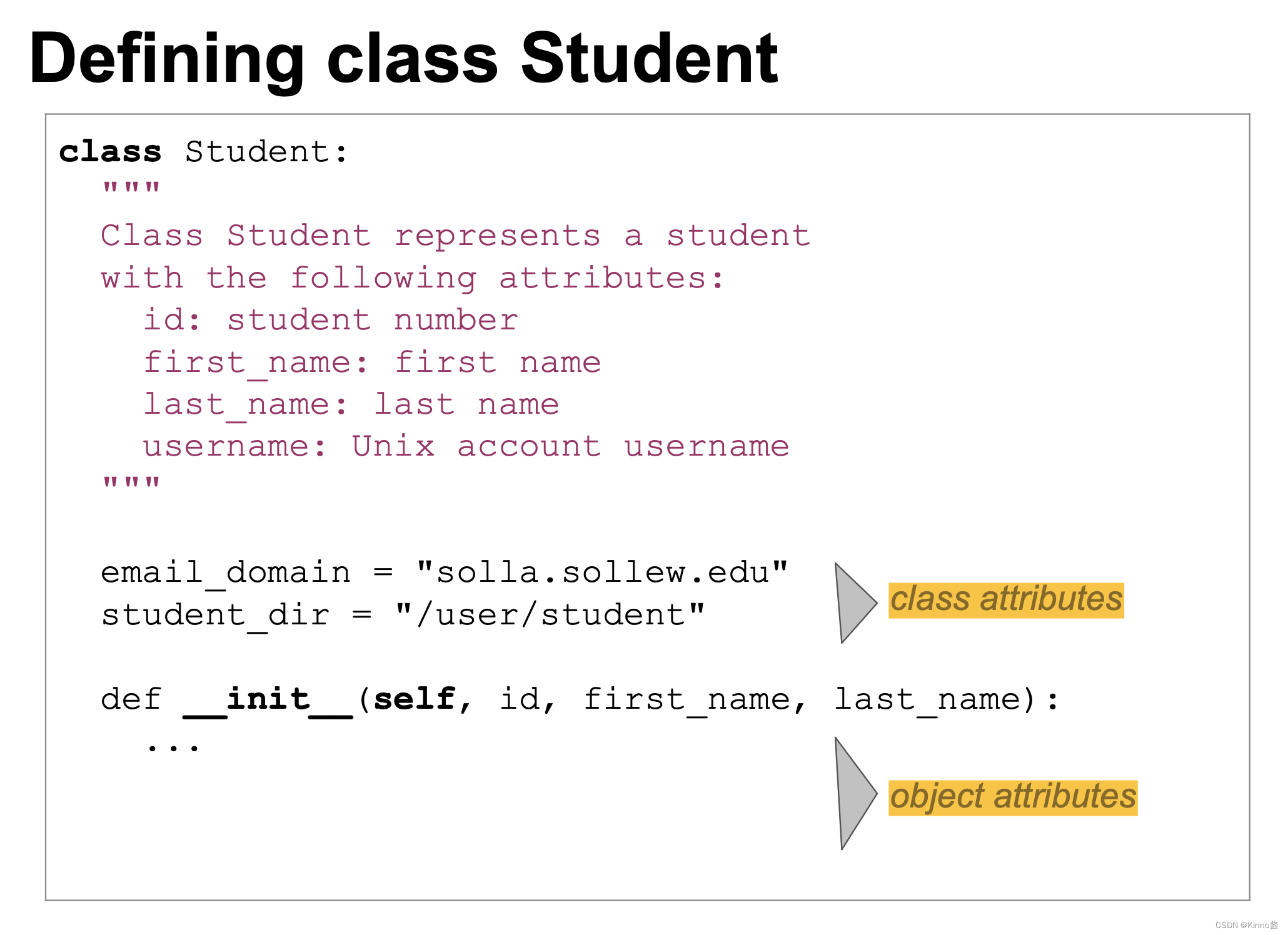
Instance attribute vs Class attribute
Some information belongs to individual object instance.
Some other information is common to all objects.
- Instance attribute: data belongs to individual object instance.
- Class attribute: data that is common to all objects. (Some classes do not have any class attributes.)
有些信息属于单个对象实例。
其他一些信息对于所有对象都是通用的。
- 实例属性:数据属于单个对象实例。
- 类属性:所有对象共有的数据。 (有些类没有任何类属性。)

Instance method vs Class/Static method
Instance method:
- Deal with a particular individual object instance
- The first argument (self) is always referred to the object instance
- instance method can be invoked from an object
Static / Class method:
- Do NOT deal with individual object instance
- Common to all object instances
- static/class method can be invoked from class name
实例方法:
- 处理特定的单个对象实例
- 第一个参数(self)始终引用对象实例
- 可以从对象调用实例方法
静态/类方法:
- 不处理单个对象实例
- 所有对象实例共有
- 静态/类方法可以从类名调用
Instance method


Special instance method

在 Python 中,特殊的实例方法(也称为魔术方法或魔法方法)在类中具有特殊的意义和用途。以下是你提到的几个魔术方法的解释和示例:
__init__ 方法
__init__ 方法是类的构造函数,用于初始化新创建的对象的属性。它在对象创建时自动调用。你可以使用它来设置对象的初始状态。
class TV_Program:def __init__(self, channel, title, start_time, duration):self.channel = channelself.title = titleself.start_time = start_timeself.duration = duration# 创建一个 TV_Program 对象
program = TV_Program('HBO', 'Game of Thrones', '21:00', 60)
print(program.channel) # 输出: HBO
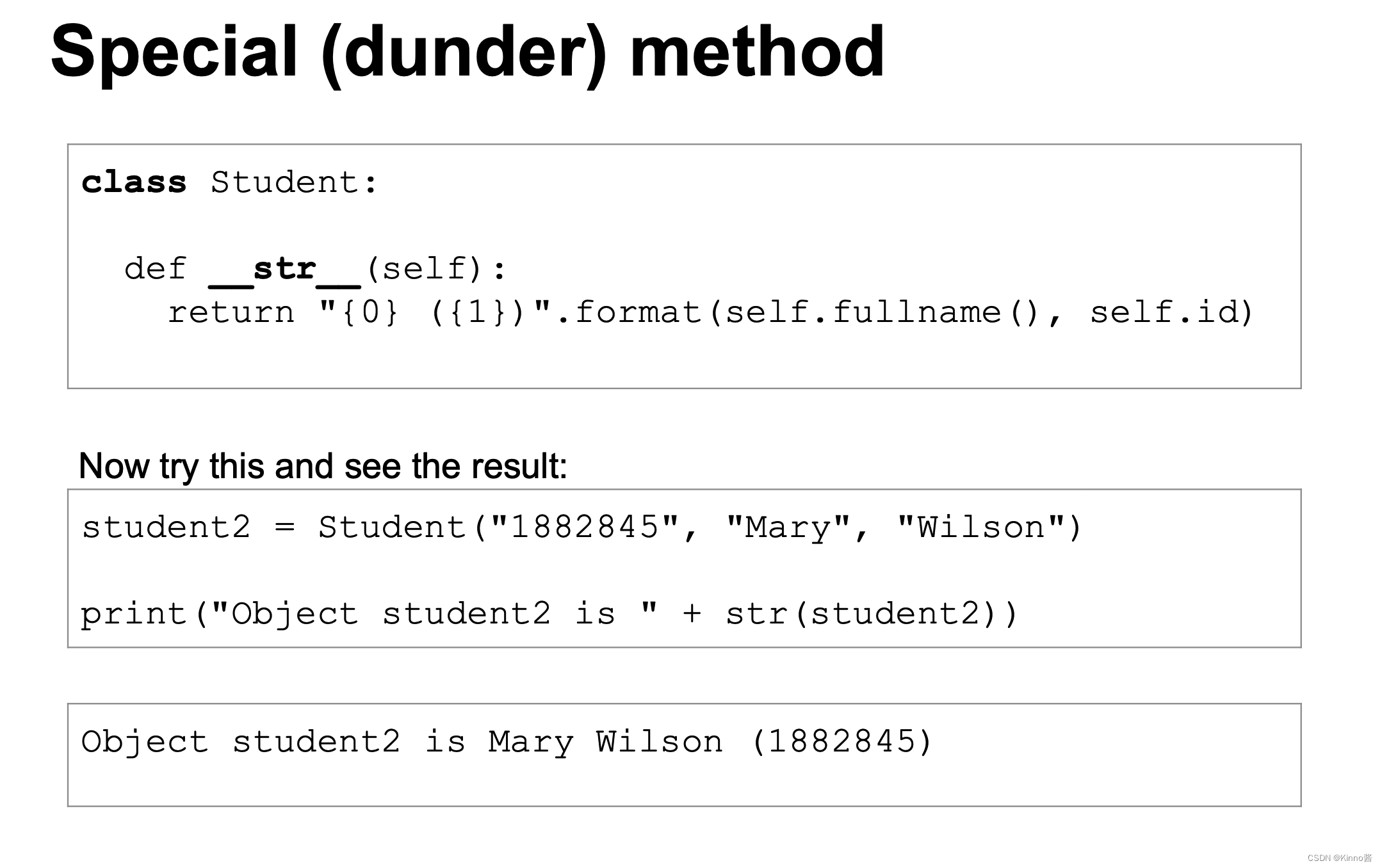
__str__ 方法
__str__ 方法用于定义对象的“可读”字符串表示。当你使用 print() 函数或 str() 函数时,Python 会调用这个方法。这个方法应该返回一个易于阅读和理解的字符串。
class TV_Program:def __init__(self, channel, title, start_time, duration):self.channel = channelself.title = titleself.start_time = start_timeself.duration = durationdef __str__(self):return f"{self.title} on {self.channel} at {self.start_time} for {self.duration} minutes"# 创建一个 TV_Program 对象
program = TV_Program('HBO', 'Game of Thrones', '21:00', 60)
print(program) # 输出: Game of Thrones on HBO at 21:00 for 60 minutes
__repr__ 方法
__repr__ 方法用于定义对象的“正式”字符串表示。这通常是一个详细且准确的字符串,应该尽可能包含信息,以便开发者可以重现该对象。__repr__ 方法通常在交互式解释器中调用,或者当使用 repr() 函数时调用。
class TV_Program:def __init__(self, channel, title, start_time, duration):self.channel = channelself.title = titleself.start_time = start_timeself.duration = durationdef __repr__(self):return f"TV_Program(channel='{self.channel}', title='{self.title}', start_time='{self.start_time}', duration={self.duration})"# 创建一个 TV_Program 对象
program = TV_Program('HBO', 'Game of Thrones', '21:00', 60)
print(repr(program)) # 输出: TV_Program(channel='HBO', title='Game of Thrones', start_time='21:00', duration=60)
完整示例
class TV_Program:def __init__(self, channel, title, start_time, duration):self.channel = channelself.title = titleself.start_time = start_timeself.duration = durationdef __str__(self):return f"{self.title} on {self.channel} at {self.start_time} for {self.duration} minutes"def __repr__(self):return f"TV_Program(channel='{self.channel}', title='{self.title}', start_time='{self.start_time}', duration={self.duration})"# 创建一个 TV_Program 对象
program = TV_Program('HBO', 'Game of Thrones', '21:00', 60)
print(program) # 调用 __str__ 方法
print(repr(program)) # 调用 __repr__ 方法
在这个示例中,__init__ 方法用于初始化 TV_Program 对象的属性,__str__ 方法用于提供对象的可读字符串表示,而 __repr__ 方法用于提供对象的正式字符串表示。
Static / Class method

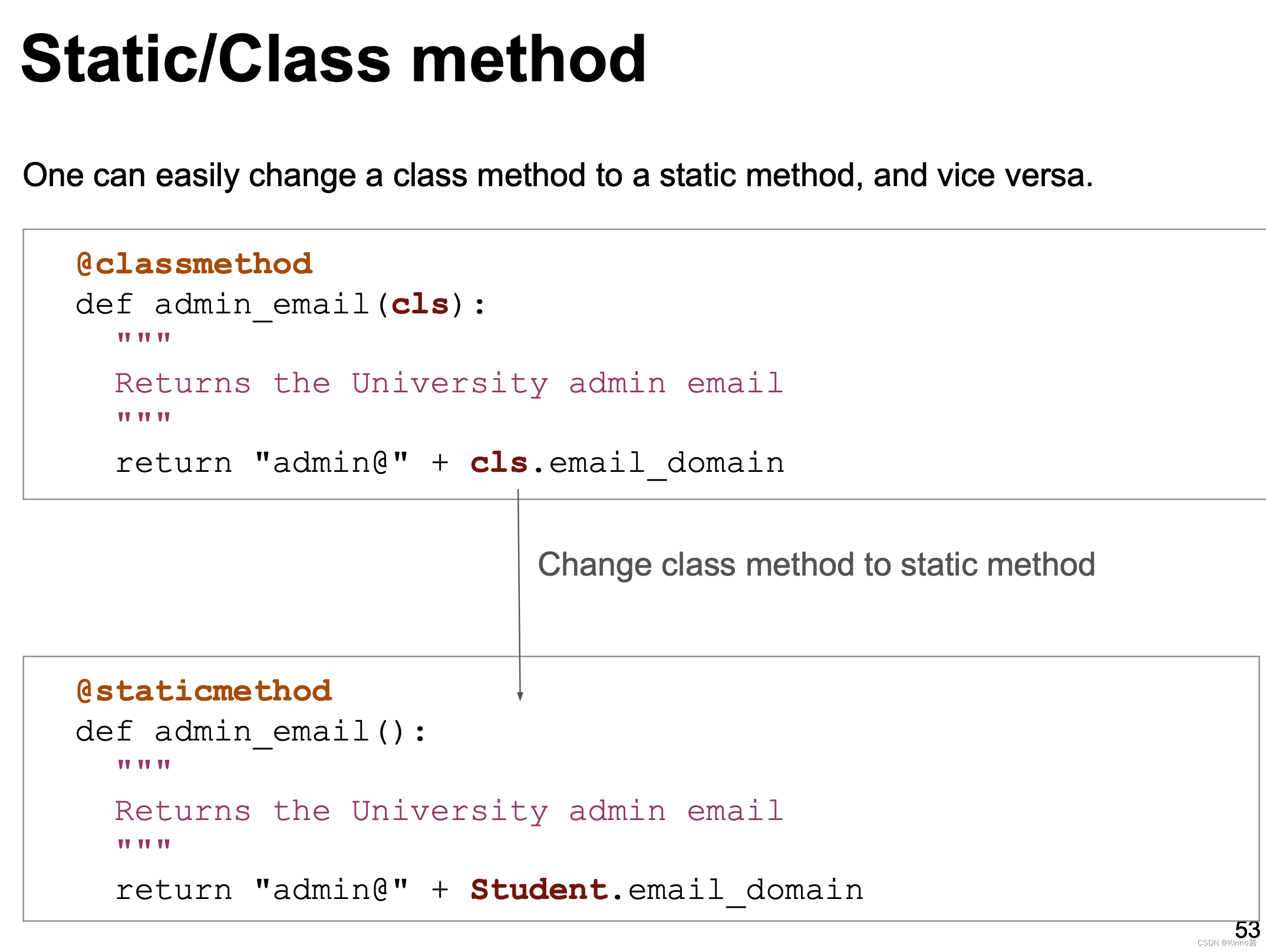
Class method vs static method: 类方法和静态方法的区别
- The first argument (cls) of a class method is always referred to the class
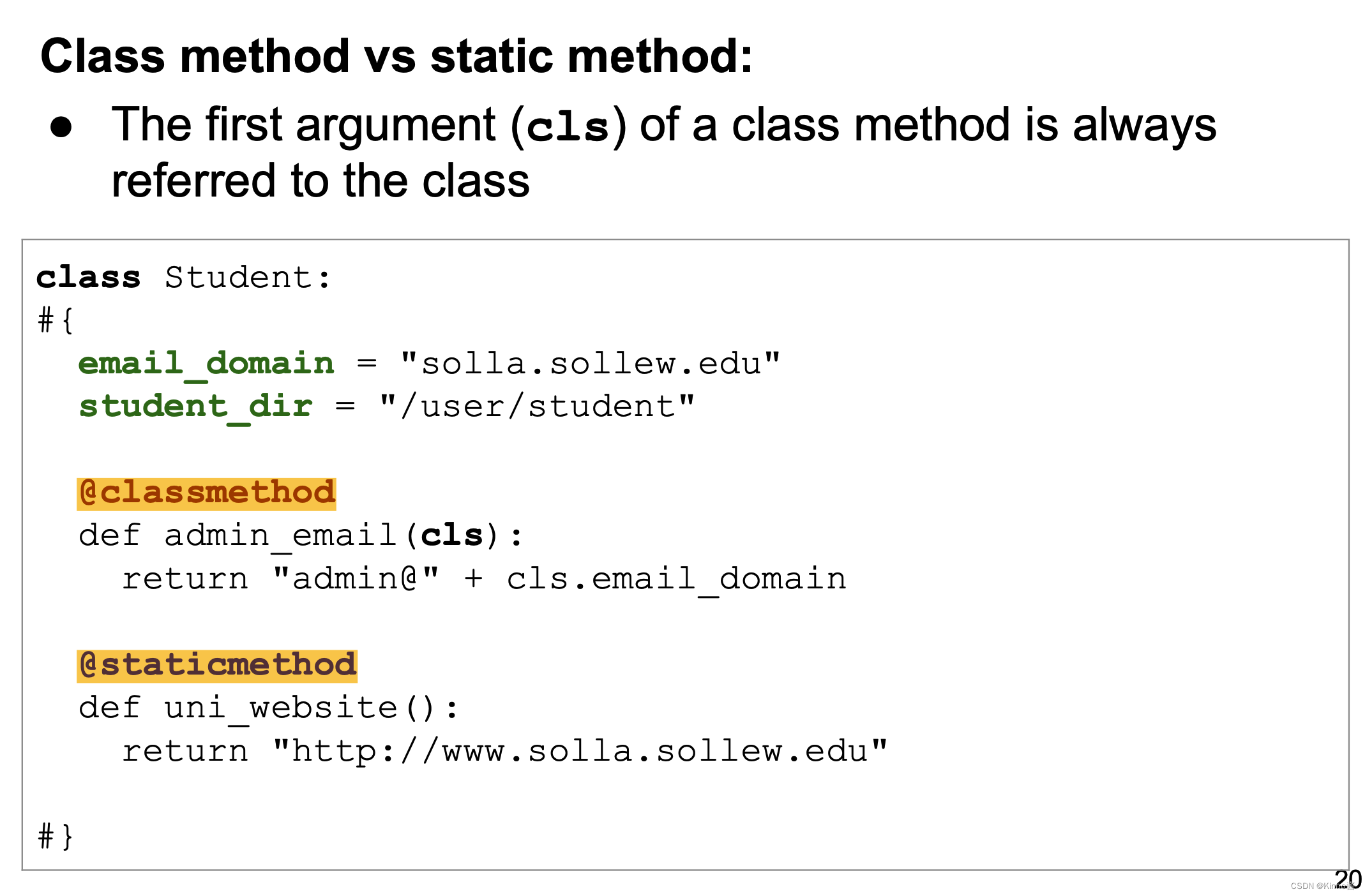
在 Python 中,类方法和静态方法都是属于类的特殊方法,但它们有不同的用途和行为。以下是它们的区别和详细解释:
类方法(Class Method)
类方法使用 @classmethod 装饰器定义,第一个参数总是指向类本身,通常命名为 cls。类方法可以访问类的属性和方法,但不能直接访问实例属性。
特点:
- 第一个参数
cls代表类,而不是实例。 - 可以通过类名或者实例调用。
- 可以访问类属性和类方法,不能访问实例属性。
示例:
class Student:email_domain = "solla.sollew.edu" # 类属性@classmethoddef admin_email(cls):return "admin@" + cls.email_domain # 访问类属性# 调用类方法
print(Student.admin_email()) # 输出: admin@solla.sollew.edu# 创建实例并调用类方法
student = Student()
print(student.admin_email()) # 输出: admin@solla.sollew.edu
静态方法(Static Method)
静态方法使用 @staticmethod 装饰器定义。静态方法没有默认的参数,它们与类和实例都无关,不能访问类属性或实例属性。静态方法通常用于一些逻辑上与类相关,但不需要访问类或实例的任何数据的方法。
特点:
- 没有默认的参数(没有
self或cls)。 - 可以通过类名或者实例调用。
- 无法访问类属性和实例属性。
示例:
class Student:email_domain = "solla.sollew.edu" # 类属性@staticmethoddef uni_website():return "http://www.solla.sollew.edu" # 逻辑上与类相关,但不访问类或实例的数据# 调用静态方法
print(Student.uni_website()) # 输出: http://www.solla.sollew.edu# 创建实例并调用静态方法
student = Student()
print(student.uni_website()) # 输出: http://www.solla.sollew.edu
示例代码:
总结:
- 类方法 使用
@classmethod装饰,第一个参数cls代表类本身,可以通过类名或实例调用,能访问类属性和类方法。 - 静态方法 使用
@staticmethod装饰,没有默认参数,不能访问类属性或实例属性,只是逻辑上与类相关的方法。
class Student:email_domain = "solla.sollew.edu" # 类属性student_dir = "/user/student" # 类属性@classmethoddef admin_email(cls):return "admin@" + cls.email_domain # 类方法,访问类属性@staticmethoddef uni_website():return "http://www.solla.sollew.edu" # 静态方法,不访问类或实例数据# 调用类方法和静态方法
print(Student.admin_email()) # 输出: admin@solla.sollew.edu
print(Student.uni_website()) # 输出: http://www.solla.sollew.edu# 创建实例并调用类方法和静态方法
student = Student()
print(student.admin_email()) # 输出: admin@solla.sollew.edu
print(student.uni_website()) # 输出: http://www.solla.sollew.edu

Defining class and creating object 定义类和创建对象

Accessing object instance attributes 访问对象的实例属性

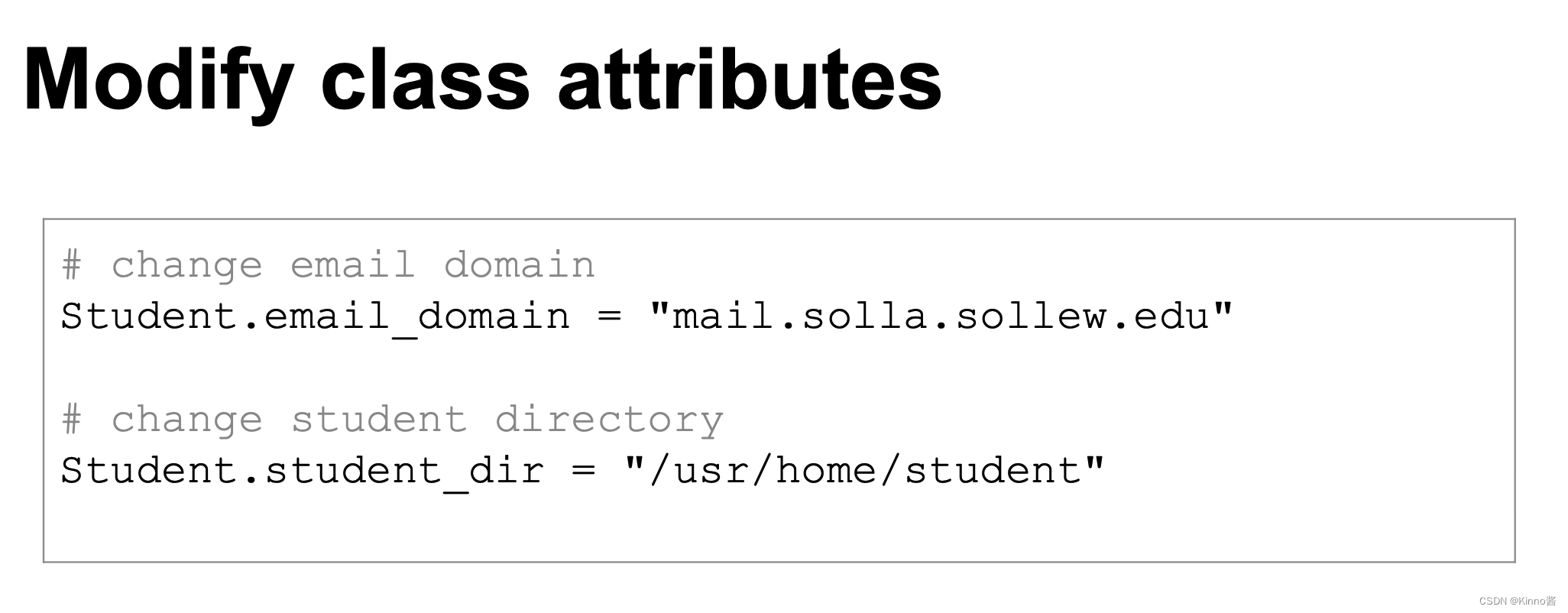
Modify object instance attributes 更改对象的实例属性

Defining an object instance method 定义对象的示例属性

类注释和函数注释

案例学习:定义一个学生类








Class inheritance 类继承

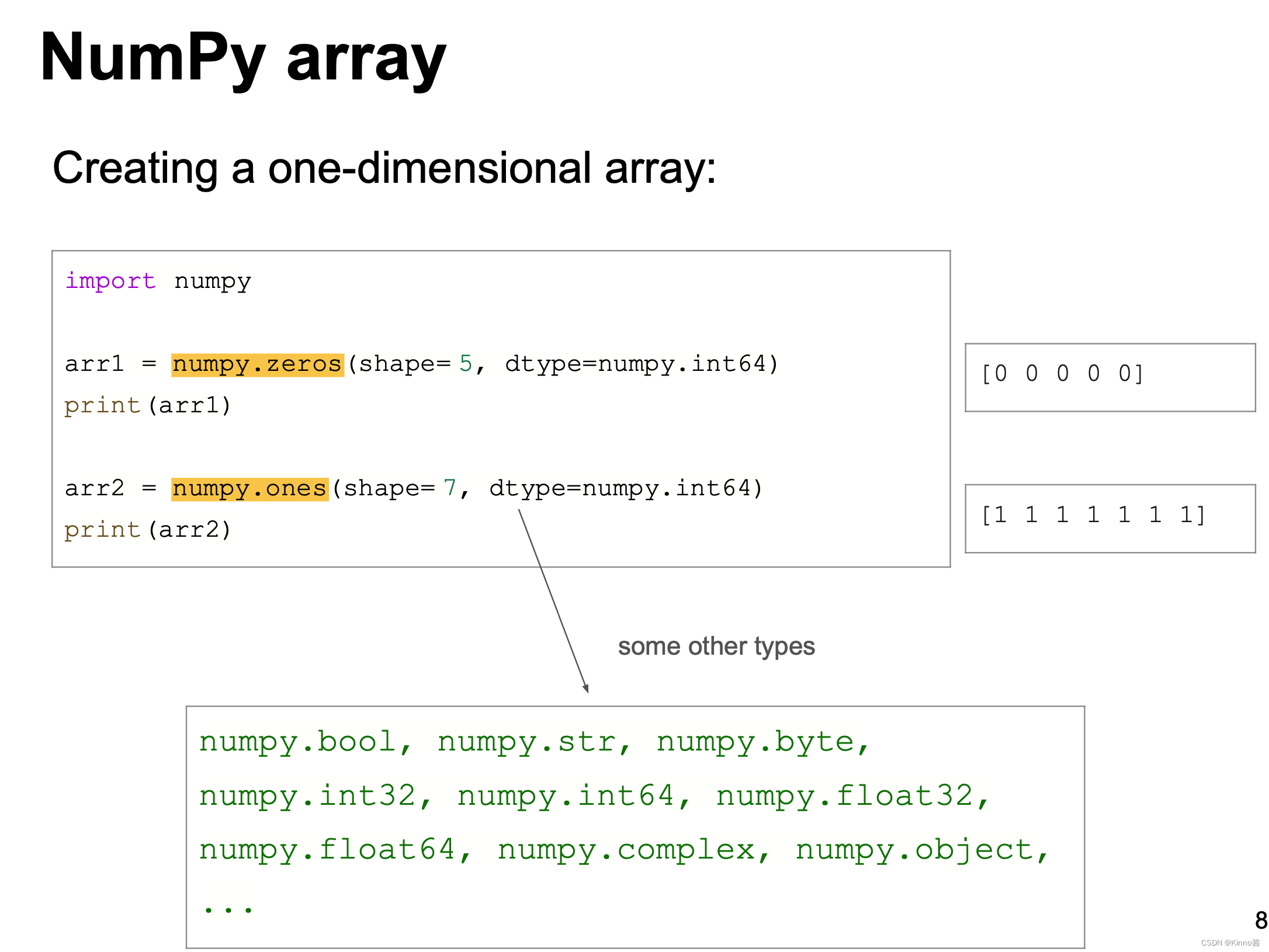
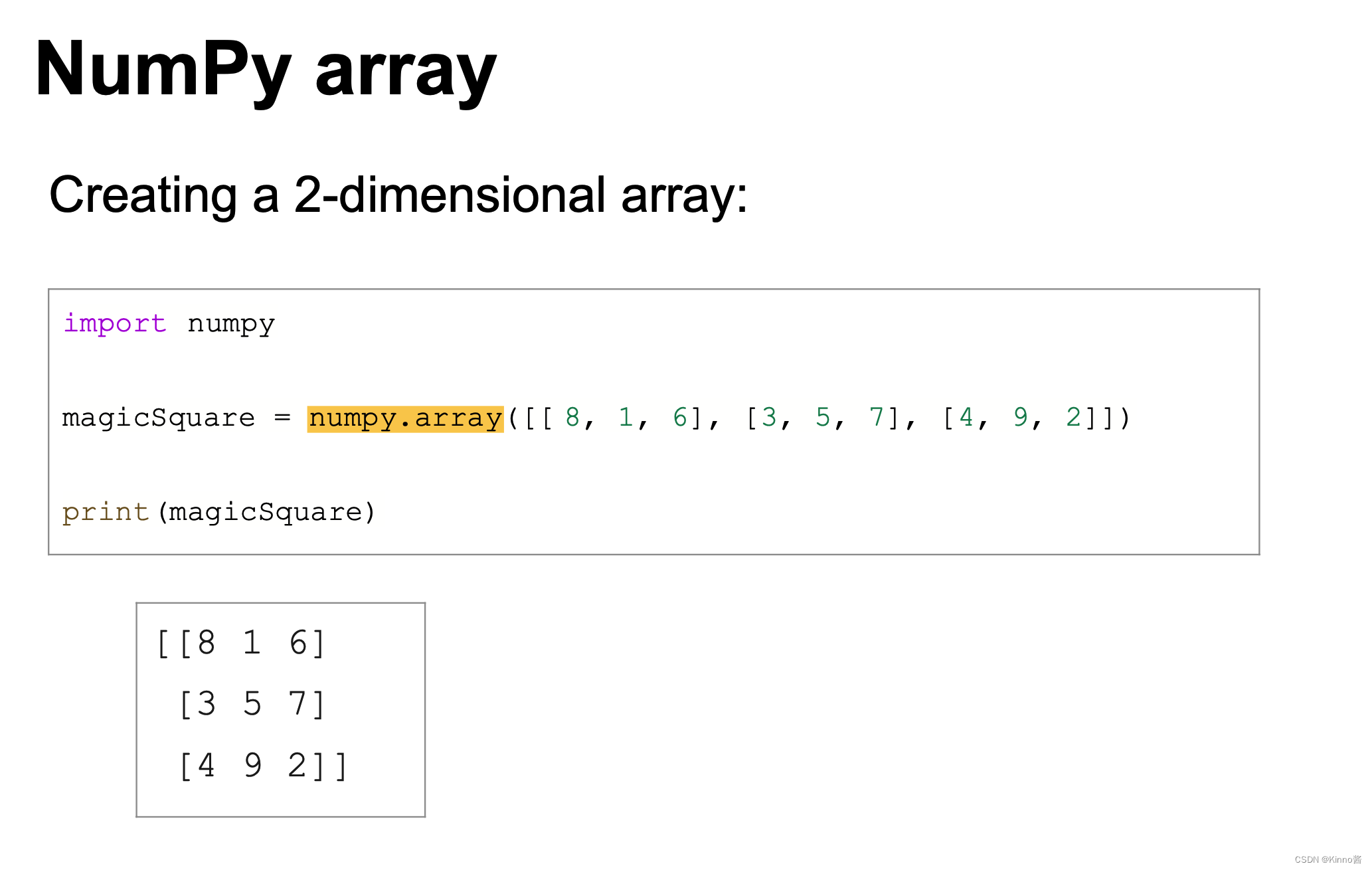
Array and Linked List
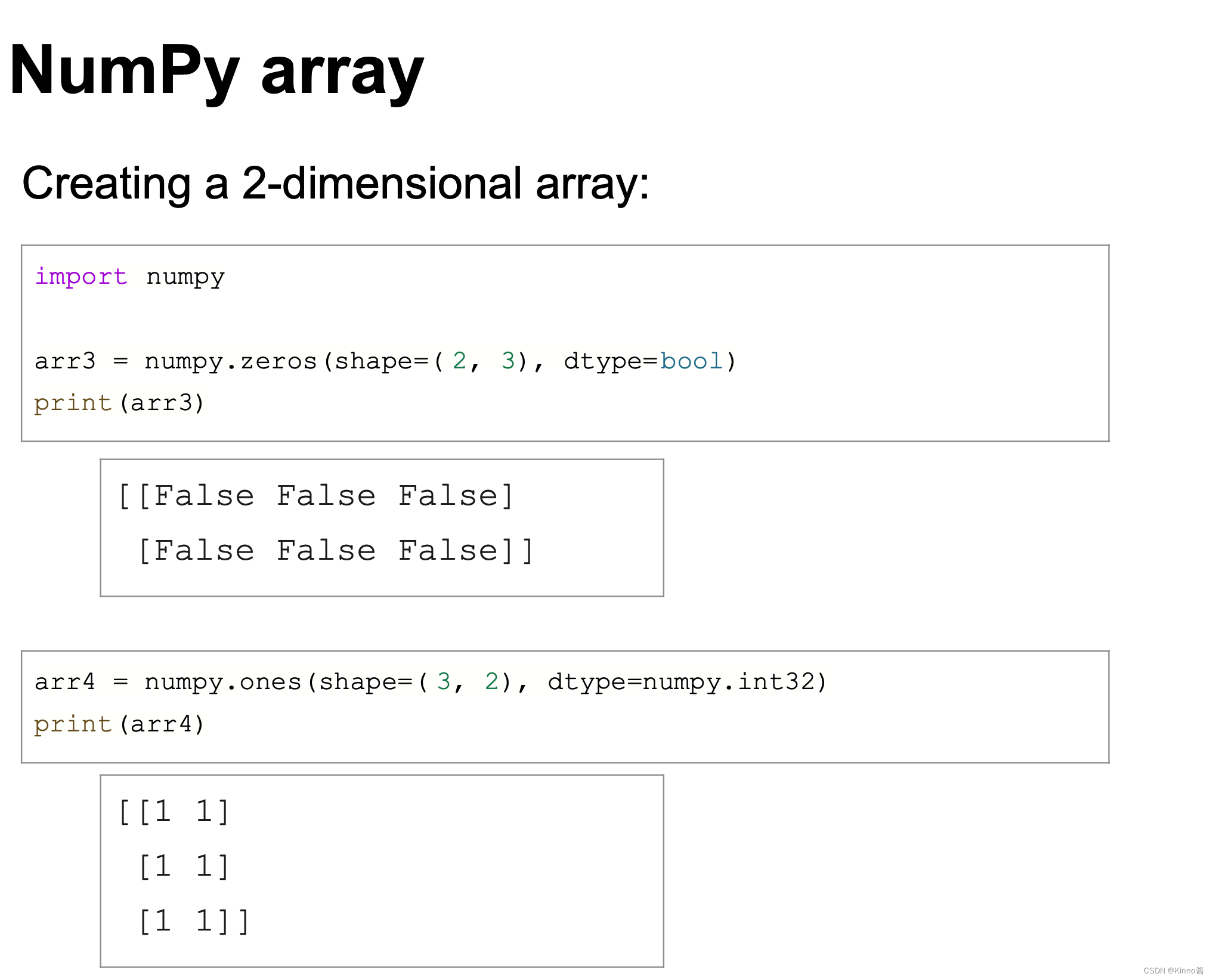
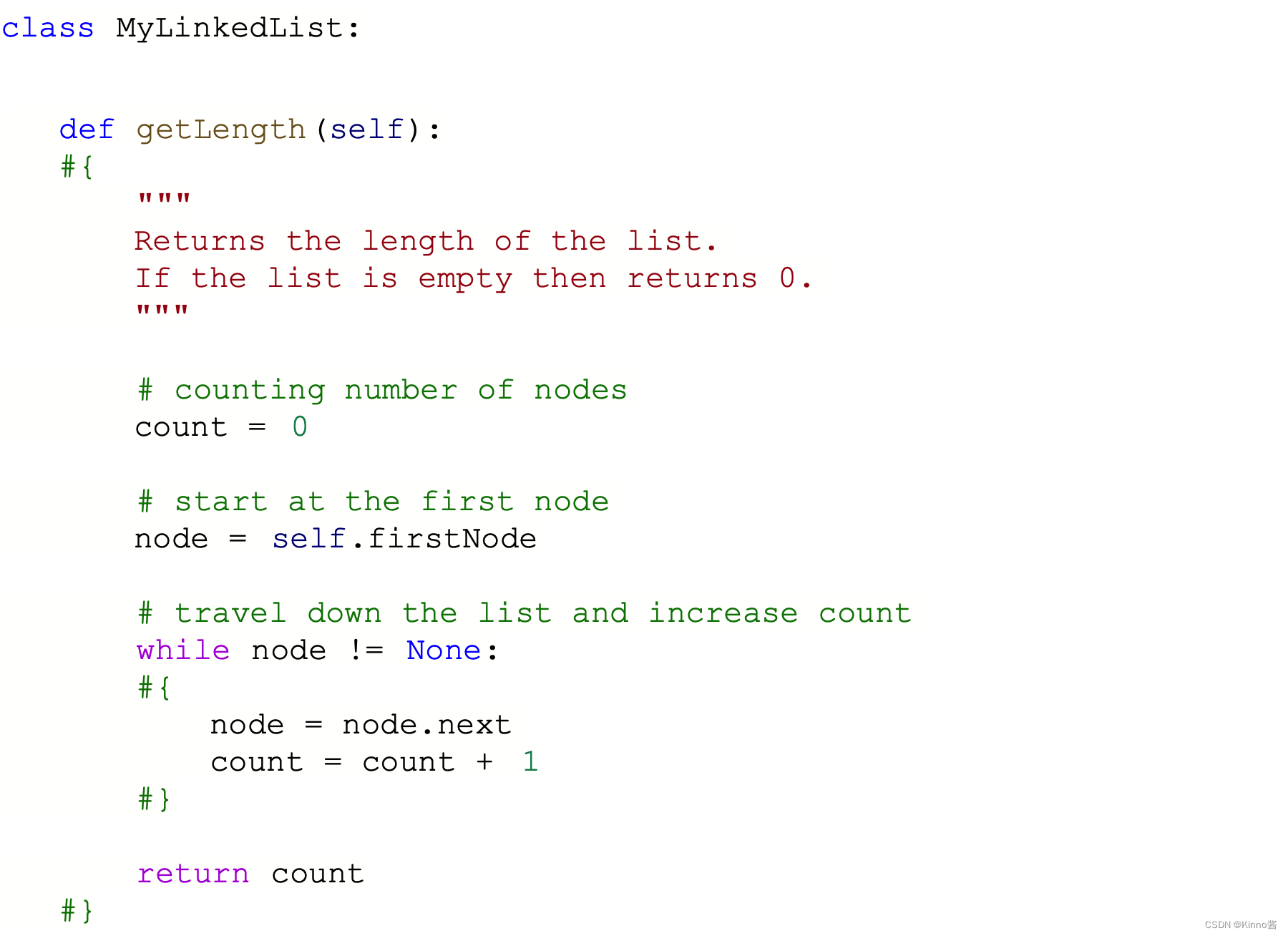
Numpy Array

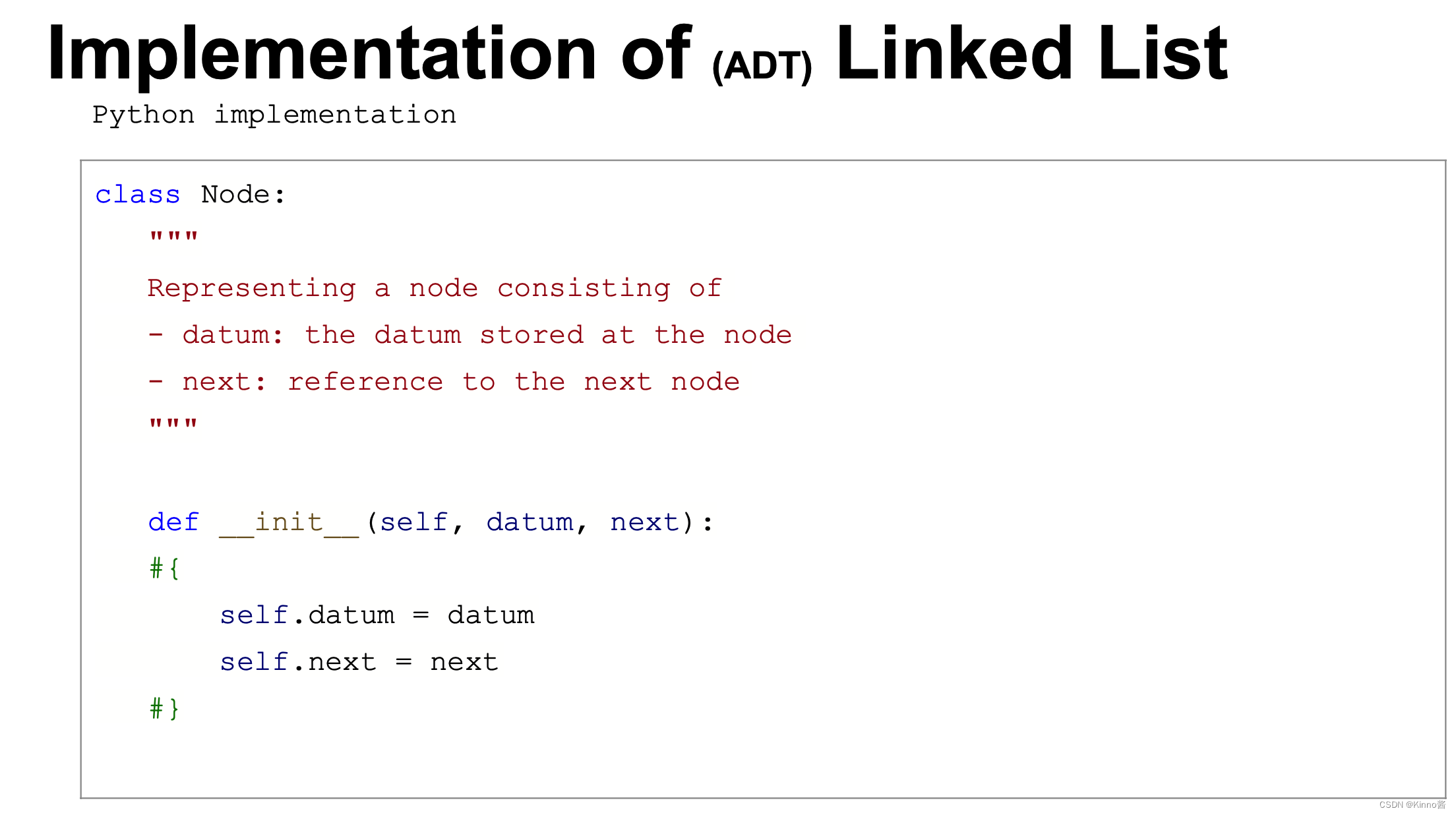
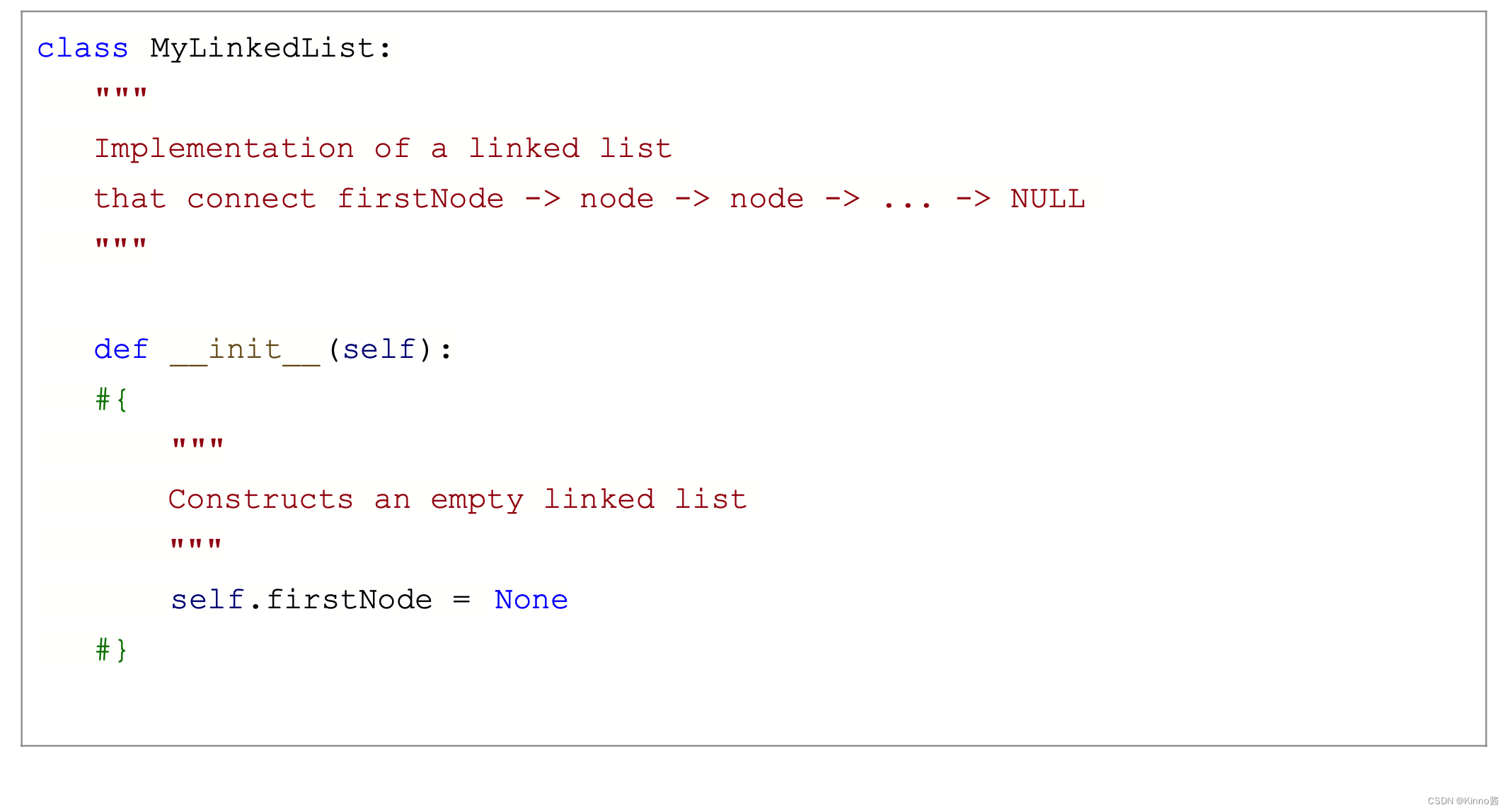
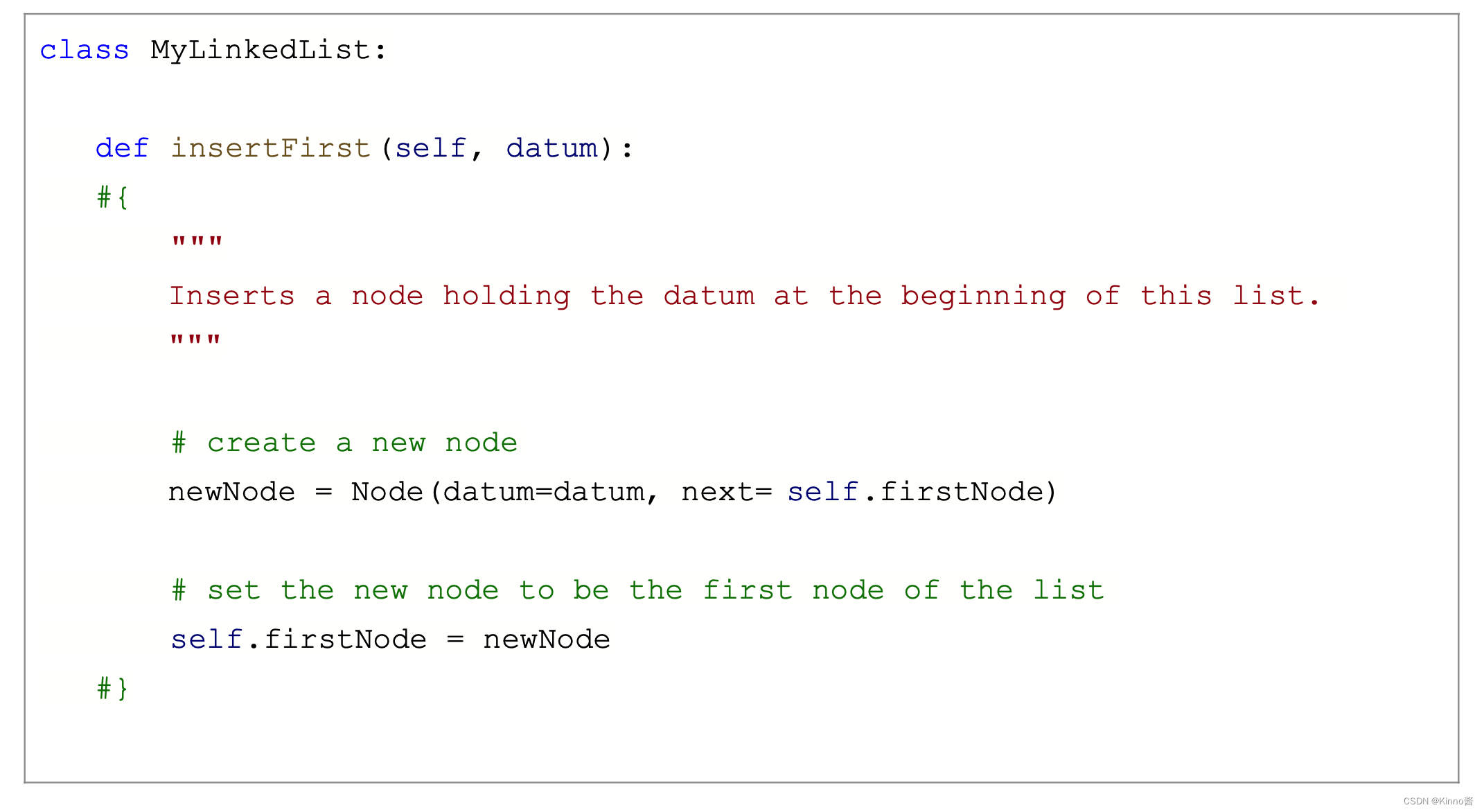
Python链表实现



Debuging
Exception&traceback

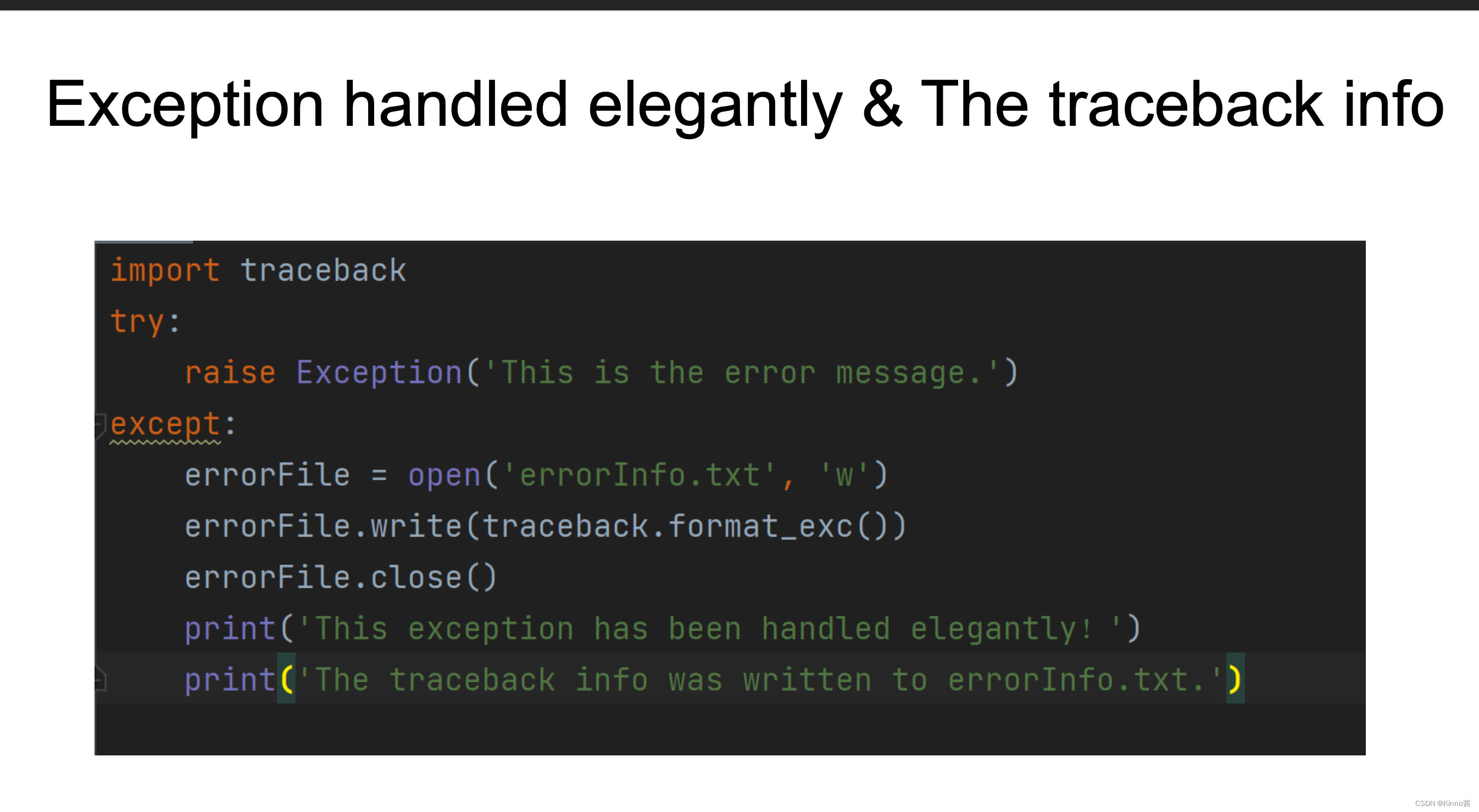
traceback库中的traceback.format_exc()获取异常追踪的详细信息
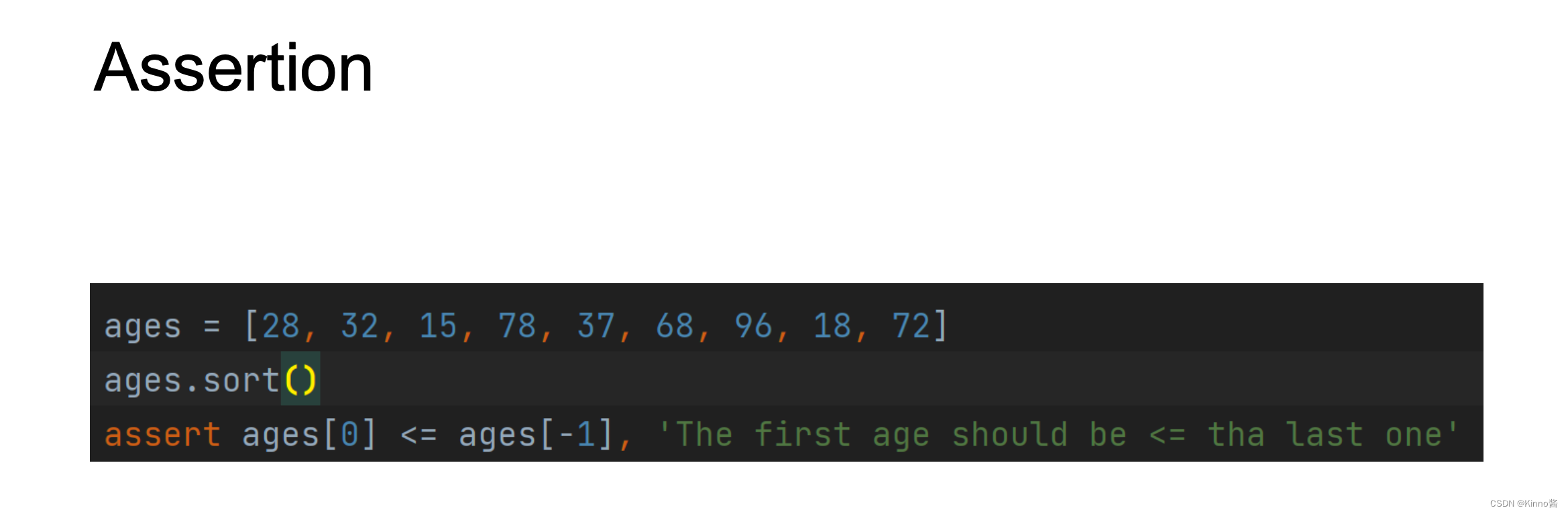
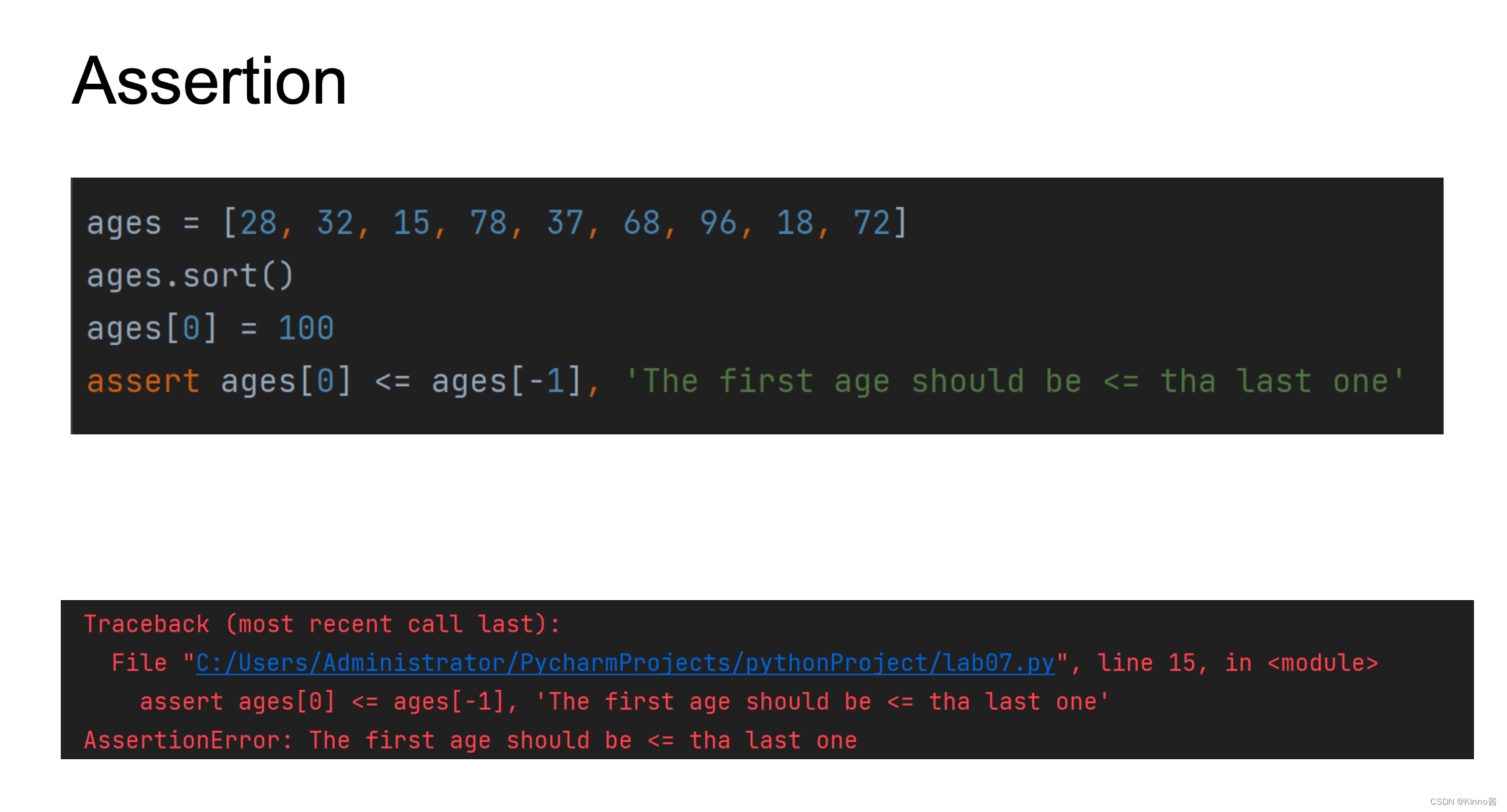
Assertion
• 它通常用于检查不可能发生的情况
• 断言语句导致终止
立即停止 → 快速失败
• 对于来自程序员而不是用户的错误
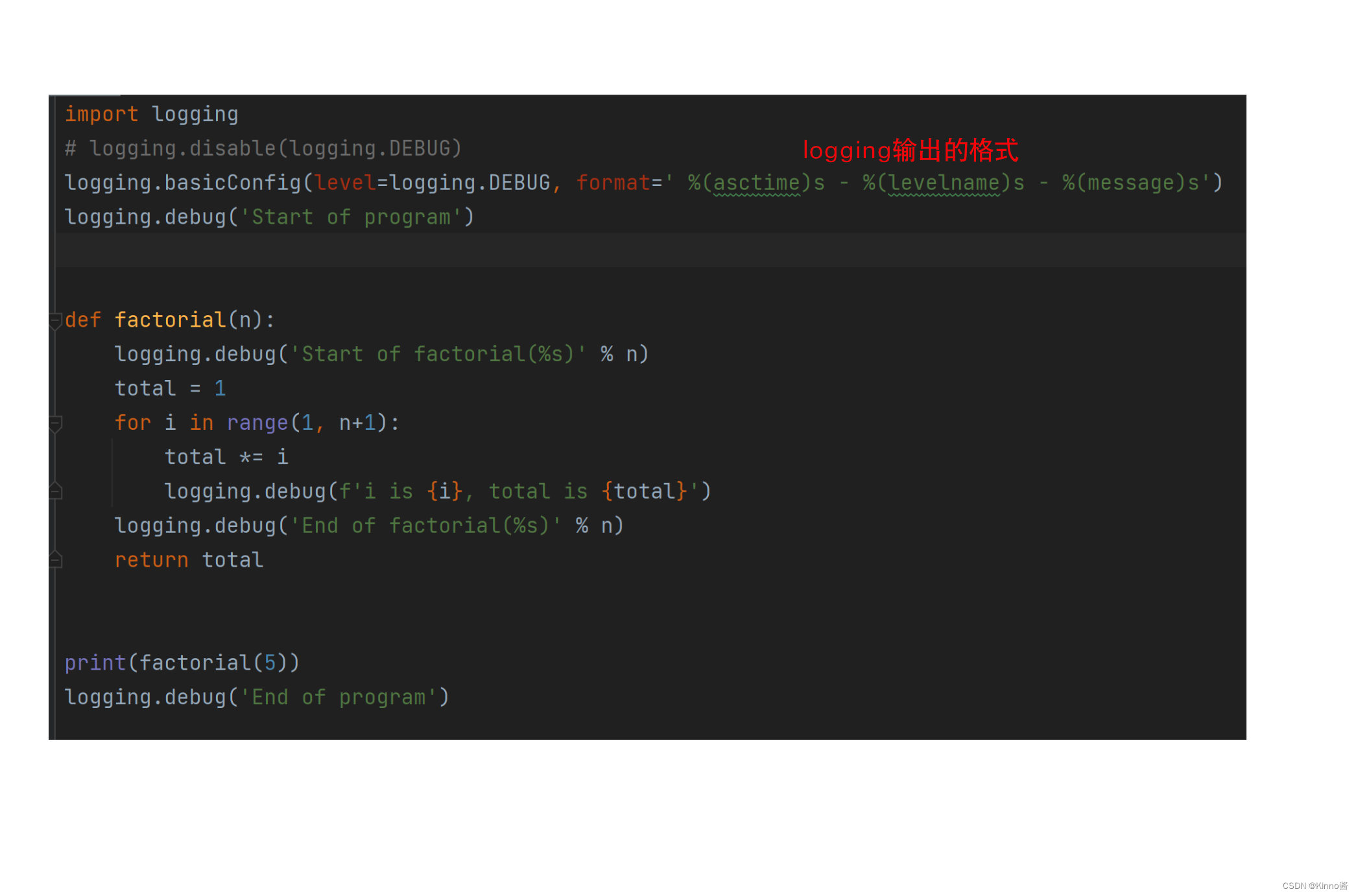
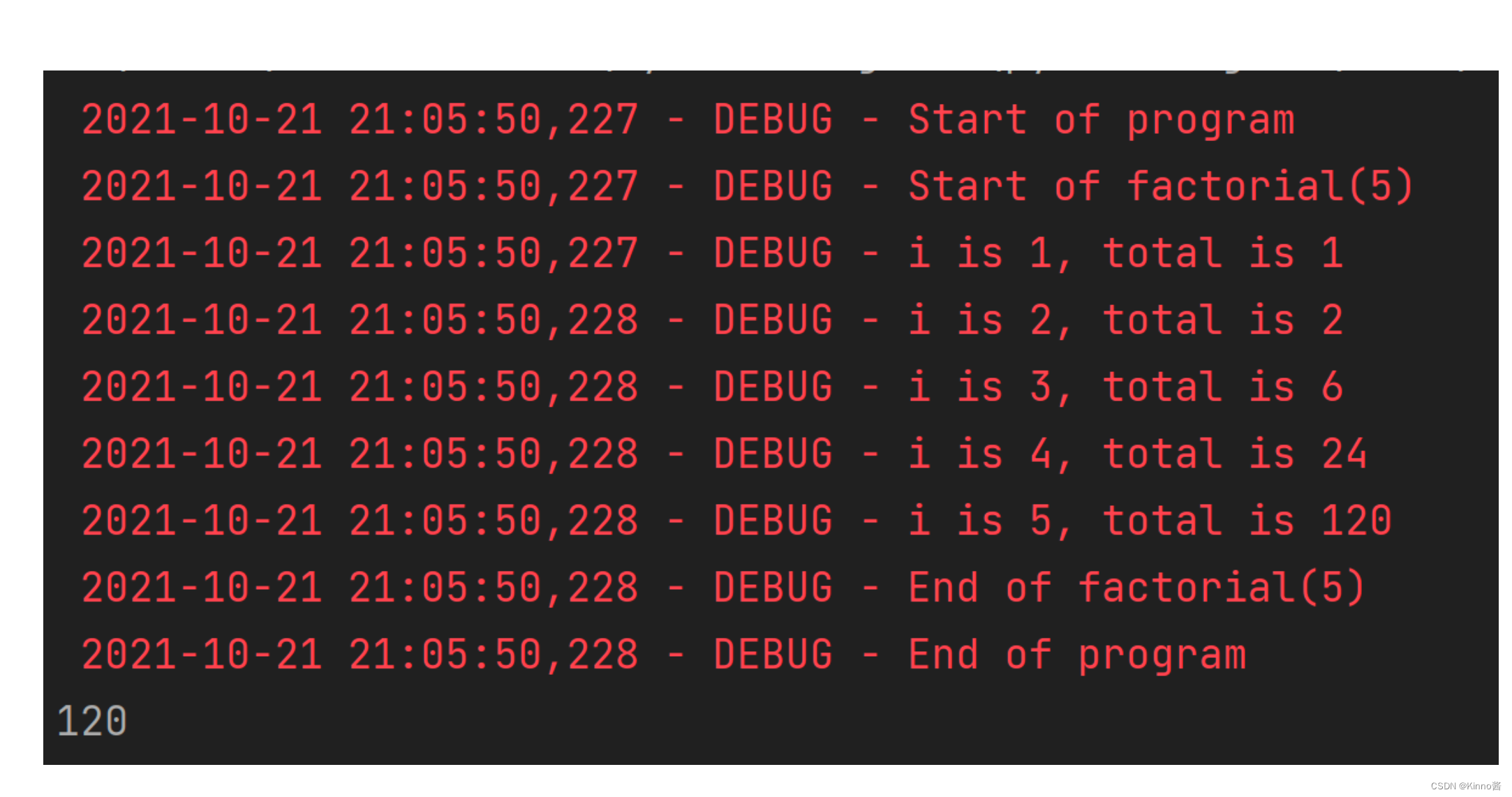
Logging
- 使用 print() 向用户显示某些变量的值显示消息
- Logging日志模块在屏幕上显示日志信息/向程序员显示信息文件